Country Summary
Introduction
Background
Samoans settled Niue in about A.D. 900, followed by Tongans around 1500. In 1889, tribal chiefs asked the UK for protectorate status, which was granted in 1900. In 1901, Niue was annexed to New Zealand as part of the Cook Islands. Niue became self-governing in 1974, in free association with New Zealand, which is responsible for its defense and foreign affairs.
Geography
Area
total: 260 sq km
land: 260 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Climate
tropical; modified by southeast trade winds
Natural resources
arable land, fish
People and Society
Population
2,000 (July 2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Niuean 65.4%, part-Niuean 14%, non-Niuean 20.6% (2017 est.)
Languages
Niuean (official) 46% (a Polynesian language closely related to Tongan and Samoan), Niuean and English 32%, English (official) 11%, Niuean and others 5%, other 6% (2011 est.)
Religions
Ekalesia Niue (Congregational Christian Church of Niue - a Protestant church founded by missionaries from the London Missionary Society) 61.7%, Church of Jesus Christ 8.7%, Roman Catholic 8.4%, Jehovah's Witness 2.7%, Seventh Day Adventist 1.4%, other 8.2%, none 8.9% (2017 est.)
Population growth rate
-0.03% (2021 est.)
Government
Government type
parliamentary democracy
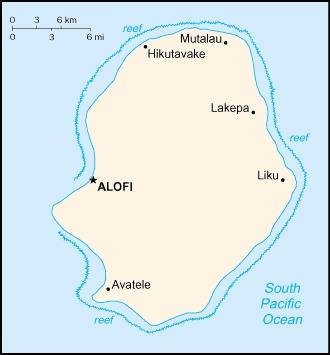
Capital
name: Alofi
Executive branch
chief of state: King CHARLES III (since 8 September 2022); represented by Governor-General of New Zealand Cindy KIRO (since 21 October 2021); the UK and New Zealand are represented by New Zealand High Commissioner Helen TUNNAH (since July 2020)
head of government: Premier Dalton TAGELAGI (since 10 June 2020)
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Assembly or Fono Ekepule (20 seats; 14 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 6 directly elected from the National Register or "common roll" by majority vote; members serve 3-year terms)
Economy
Economic overview
upper-middle-income self-governing New Zealand territorial economy; massive emigration; postage stamps, small-scale agricultural processing, and subsistence farming; depends on New Zealand subsidies; EU preferential market access not utilized
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$10.01 million (2003 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$5,800 (2003 est.)
Agricultural products
coconuts, taro, fruit, sweet potatoes, tropical fruit, yams, vegetables, lemons, limes, bananas
Industries
handicrafts, food processing
Exports
$201,400 (2004 est.)
Exports - partners
Indonesia 92%, South Korea 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
tanker ships, fruit juice, thermostats, textiles, measurement devices/appliances (2019)
Imports
$9.038 million (2004 est.)
Imports - partners
New Zealand 43%, United Kingdom 30%, Japan 22% (2019)
Imports - commodities
hydraulic engines, ships, refined petroleum, cars, plastics (2019)
Exchange rates
New Zealand dollars (NZD) per US dollar -
Page last updated: Monday, September 12, 2022
