Introduction
Background
Timor was actively involved in Southeast Asian trading networks for centuries and by the 14th century exported aromatic sandalwood, slaves, honey, and wax. By mid-16th century, the Portuguese had colonized the island. It was incorporated into Indonesia in July 1976 as the province of Timor Timur (East Timor). On 20 May 2002, Timor-Leste was internationally recognized as an independent state.
Geography
Area
total: 14,874 sq km
land: 14,874 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Climate
tropical; hot, humid; distinct rainy and dry seasons
Natural resources
gold, petroleum, natural gas, manganese, marble
People and Society
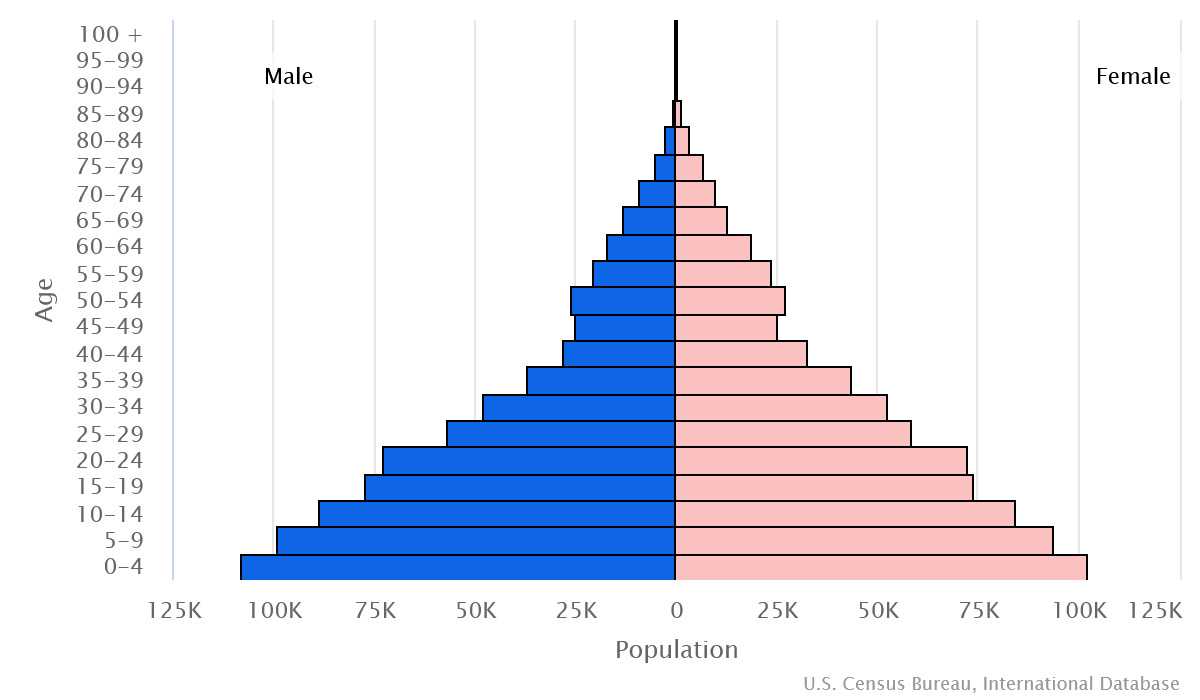
Population
total: 1,506,909
male: 750,665
female: 756,244 (2024 est.)
Ethnic groups
Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian) (includes Tetun, Mambai, Tokodede, Galoli, Kemak, Baikeno), Melanesian-Papuan (includes Bunak, Fataluku, Bakasai), small Chinese minority
Languages
Tetun Prasa 30.6%, Mambai 16.6%, Makasai 10.5%, Tetun Terik 6.1%, Baikenu 5.9%, Kemak 5.8%, Bunak 5.5%, Tokodede 4%, Fataluku 3.5%, Waima'a 1.8%, Galoli 1.4%, Naueti 1.4%, Idate 1.2%, Midiki 1.2%, other 4.5% (2015 est.)
Religions
Roman Catholic 97.6%, Protestant/Evangelical 2%, Muslim 0.2%, other 0.2% (2015 est.)
Population growth rate
2.04% (2024 est.)
Government
Government type
semi-presidential republic
Capital
name: Dili
Executive branch
chief of state: President José RAMOS-HORTA (since 20 May 2022); note - the president is commander in chief of the military and can veto legislation, dissolve parliament, and call national elections
head of government: Prime Minister Kay Rala Xanana GUSMAO (since 1 July 2023)
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Parliament (65 seats; members directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by closed, party-list proportional representation vote using the D'Hondt method to serve 5-year terms)
Economy
Economic overview
lower middle-income Southeast Asian economy; government expenditures funded via oil fund drawdowns; endemic corruption undermines growth; foreign aid-dependent; wide-scale poverty, unemployment, and illiteracy
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$5.289 billion (2022 est.)
$6.656 billion (2021 est.)
$6.32 billion (2020 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$3,900 (2022 est.)
$5,000 (2021 est.)
$4,900 (2020 est.)
Agricultural products
maize, rice, coconuts, root vegetables, vegetables, cassava, other meats, coffee, beans, pork (2022)
Industries
printing, soap manufacturing, handicrafts, woven cloth
Exports
$1.858 billion (2022 est.)
$2.772 billion (2021 est.)
$1.598 billion (2020 est.)
Exports - partners
China 25%, Indonesia 20%, Japan 14%, South Korea 13%, Thailand 7% (2022)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, coffee, natural gas, beer, construction vehicles (2022)
Imports
$1.396 billion (2022 est.)
$1.298 billion (2021 est.)
$1.486 billion (2020 est.)
Imports - partners
Indonesia 27%, China 23%, Singapore 9%, Australia 6%, Malaysia 6% (2022)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, rice, cars, coal, cranes (2022)
Page last updated: Wednesday, May 15, 2024