Azerbaijan
Introduction
Background
Azerbaijan - a secular nation with a majority-Turkic and majority-Shia Muslim population - was briefly independent (from 1918 to 1920) following the collapse of the Russian Empire; it was subsequently incorporated into the Soviet Union for seven decades. Azerbaijan remains involved in the protracted Nagorno-Karabakh conflict with Armenia. Nagorno-Karabakh was a primarily ethnic Armenian region that Moscow recognized in 1923 as an autonomous oblast within Soviet Azerbaijan. In the late Soviet period, a separatist movement developed which sought to end Azerbaijani control over the region. Fighting over Nagorno-Karabakh began in 1988 and escalated after Armenia and Azerbaijan attained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. By the time a ceasefire took effect in May 1994, separatists, with Armenian support, controlled Nagorno‑Karabakh and seven surrounding Azerbaijani territories.
Under the terms of a cease-fire agreement following Azerbaijan’s victory in the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War that took place from September-November 2020, Armenia returned to Azerbaijan the remaining territories it had occupied and also the southern part of Nagorno-Karabakh, including the culturally and historically important city that Azerbaijanis call Shusha and Armenians call Shushi. Despite Azerbaijan’s territorial gains, peace in the region remains elusive because of unsettled issues concerning the delimitation of borders, the opening of regional transportation and communication links, the status of ethnic enclaves near border regions, and the final status of the Nagorno-Karabakh region. Russian peacekeepers deployed to Nagorno-Karabakh to supervise the cease-fire for a minimum five-year term did not prevent the outbreak of sporadic, low-level military clashes along the Azerbaijan-Armenia border in 2021.
In the three decades following its independence in 1991, Azerbaijan has succeeded in significantly reducing the poverty rate and has directed revenues from its oil and gas production to develop the country’s infrastructure. However, corruption remains a burden on the economy, and Western observers and members of the country’s political opposition have accused the government of authoritarianism, pointing to elections that are neither free nor fair, state control of the media, and the systematic abuse of human rights targeting individuals and groups who are perceived as threats to the administration. The country’s leadership has remained in the ALIYEV family since Heydar ALIYEV, formerly the most highly ranked Azerbaijani member of the Communist Party during the Soviet period, became president in the midst of the first Nagorno-Karabakh War in 1993. Heydar ALIYEV groomed his son to succeed him, and Ilham ALIYEV subsequently became president in 2003. As a result of two national referendums that eliminated presidential term limits and extended the presidential term from 5 to 7 years, President ALIYEV secured a fourth term in April 2018 in an election that international observers noted had serious shortcomings. Reforms are underway to diversify the country’s economy away from its dependence on oil and gas; additional reforms are needed to address weaknesses in government institutions, particularly in the education and health sectors, and the court system.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
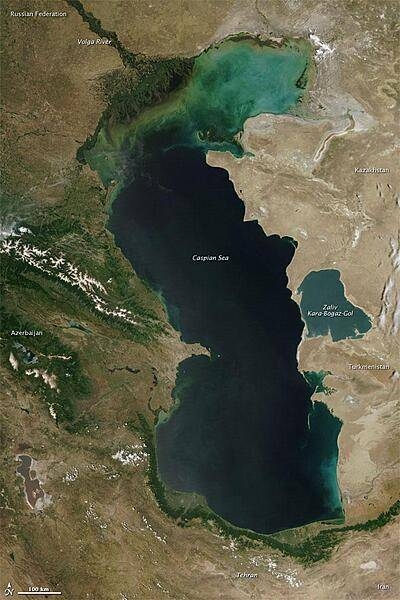
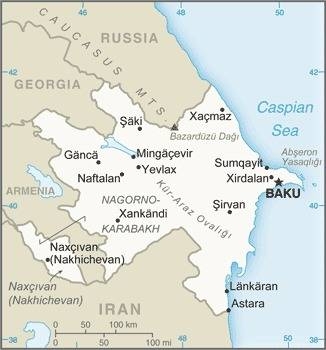
Southwestern Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea, between Iran and Russia, with a small European portion north of the Caucasus range
Geographic coordinates
40 30 N, 47 30 E
Map references
Asia
Area
total: 86,600 sq km
land: 82,629 sq km
water: 3,971 sq km
note: includes the exclave of Naxcivan Autonomous Republic and the Nagorno-Karabakh region; the region's autonomy was abolished by Azerbaijani Supreme Soviet on 26 November 1991
Area - comparative
about three-quarters the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Maine
Land boundaries
total: 2,468 km
border countries (5): Armenia 996 km; Georgia 428 km; Iran 689 km; Russia 338 km; Turkey 17 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked); note - Azerbaijan borders the Caspian Sea (713 km)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
dry, semiarid steppe
Terrain
large, flat Kur-Araz Ovaligi (Kura-Araks Lowland, much of it below sea level) with Great Caucasus Mountains to the north, Qarabag Yaylasi (Karabakh Upland) to the west; Baku lies on Abseron Yasaqligi (Apsheron Peninsula) that juts into Caspian Sea
Elevation
highest point: Bazarduzu Dagi 4,466 m
lowest point: Caspian Sea -28 m
mean elevation: 384 m
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, nonferrous metals, bauxite
Land use
agricultural land: 57.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 22.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2.7% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 32.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 11.3% (2018 est.)
other: 31.1% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
14,649 sq km (2020)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Caspian Sea (shared with Iran, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Kazakhstan) - 374,000 sq km
Population distribution
highest population density is found in the far eastern area of the country, in and around Baku; apart from smaller urbanized areas, the rest of the country has a fairly light and evenly distributed population
Natural hazards
droughts
Geography - note
both the main area of the country and the Naxcivan exclave are landlocked
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Azerbaijani(s)
adjective: Azerbaijani
Ethnic groups
Azerbaijani 91.6%, Lezghin 2%, Russian 1.3%, Armenian 1.3%, Talysh 1.3%, other 2.4% (2009 est.)
note: the Nagorno-Karabakh region, which is part of Azerbaijan on the basis of the borders recognized when the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991, is populated almost entirely by ethnic Armenians; Azerbaijan has over 80 ethnic groups
Languages
Azerbaijani (Azeri) (official) 92.5%, Russian 1.4%, Armenian 1.4%, other 4.7% (2009 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Dünya fakt kitabı, əsas məlumatlar üçün əvəz olunmaz mənbədir (Azerbaijani)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: Russian is widely spoken
Religions
Muslim 97.3% (predominantly Shia), Christian 2.6%, other <0.1, unaffiliated <0.1 (2020 est.)
note: religious affiliation for the majority of Azerbaijanis is largely nominal, percentages for actual practicing adherents are probably much lower
Demographic profile
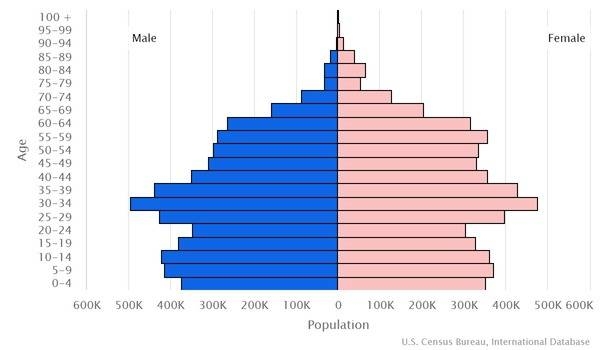
Azerbaijan’s citizenry has over 80 ethnic groups. The far eastern part of the country has the highest population density, particularly in and around Baku. Apart from smaller urbanized areas, the rest of the country has a fairly light and evenly distributed population. Approximately 57% of the country’s inhabitants lives in urban areas. While the population is continuing to grow, it is in the early stages of aging. The declining fertility rate – which has decreased from about 5.5 children per woman in the 1950s to less than the 2.1 replacement level in 2022 – combined with increasing life expectancy has resulted in the elderly making up a larger share of Azerbaijan’s populace. The percentage of elderly residents and the slowed growth and eventual shrinkage of the working-age population could put pressure on the country’s pension and healthcare systems.
Age structure
0-14 years: 22.84% (male 1,235,292/female 1,095,308)
15-24 years: 13.17% (male 714,718/female 629,494)
25-54 years: 45.29% (male 2,291,600/female 2,330,843)
55-64 years: 11.41% (male 530,046/female 634,136)
65 years and over: 7.29% (male 289,604/female 454,769) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 44.2
youth dependency ratio: 34.7
elderly dependency ratio: 9.7
potential support ratio: 10.3 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 32.6 years
male: 31.1 years
female: 34.2 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
highest population density is found in the far eastern area of the country, in and around Baku; apart from smaller urbanized areas, the rest of the country has a fairly light and evenly distributed population
Urbanization
urban population: 57.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.38% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
note: data include Nagorno-Karabakh
Major urban areas - population
2.432 million BAKU (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.11 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.15 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.82 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.49 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
24 years (2019 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
26 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120Infant mortality rate
total: 23.51 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 24.62 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 22.33 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 74.15 years
male: 71.08 years
female: 77.41 years (2022 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 93.3% of population
total: 97.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 6.7% of population
total: 2.9% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
4% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
3.17 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Hospital bed density
4.8 beds/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: NA
total: NA
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: NA
total: (2020 est.) NA
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 1.38 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.36 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.06 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.94 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 24% (2020 est.)
male: 47.9% (2020 est.)
female: 0.1% (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.8%
male: 99.9%
female: 99.7% (2019)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 14 years
male: 13 years
female: 14 years (2021)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 12.4%
male: 10.9%
female: 14.2% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
local scientists consider the Abseron Yasaqligi (Apsheron Peninsula) (including Baku and Sumqayit) and the Caspian Sea to be the ecologically most devastated area in the world because of severe air, soil, and water pollution; soil pollution results from oil spills, from the use of DDT pesticide, and from toxic defoliants used in the production of cotton; surface and underground water are polluted by untreated municipal and industrial wastewater and agricultural run-off
Environment - international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 18.2 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 37.62 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 44.87 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
dry, semiarid steppe
Land use
agricultural land: 57.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 22.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2.7% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 32.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 11.3% (2018 est.)
other: 31.1% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 57.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.38% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
note: data include Nagorno-Karabakh
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.02% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2,930,349 tons (2015 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Caspian Sea (shared with Iran, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Kazakhstan) - 374,000 sq km
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 449.6 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 3.062 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 9.27 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
34.675 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Azerbaijan
conventional short form: Azerbaijan
local long form: Azarbaycan Respublikasi
local short form: Azarbaycan
former: Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
etymology: the name translates as "Land of Fire" and refers to naturally occurring surface fires on ancient oil pools or from natural gas discharges
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Baku (Baki, Baky)
geographic coordinates: 40 23 N, 49 52 E
time difference: UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: does not observe daylight savings time
etymology: the name derives from the Persian designation of the city "bad-kube" meaning "wind-pounded city" and refers to the harsh winds and severe snow storms that can hit the city
note: at approximately 28 m below sea level, Baku's elevation makes it the lowest capital city in the world
Administrative divisions
66 districts (rayonlar; rayon - singular), 11 cities (saharlar; sahar - singular);
rayons: Abseron, Agcabadi, Agdam, Agdas, Agstafa, Agsu, Astara, Babak, Balakan, Barda, Beylaqan, Bilasuvar, Cabrayil, Calilabad, Culfa, Daskasan, Fuzuli, Gadabay, Goranboy, Goycay, Goygol, Haciqabul, Imisli, Ismayilli, Kalbacar, Kangarli, Kurdamir, Lacin, Lankaran, Lerik, Masalli, Neftcala, Oguz, Ordubad, Qabala, Qax, Qazax, Qobustan, Quba, Qubadli, Qusar, Saatli, Sabirabad, Sabran, Sadarak, Sahbuz, Saki, Salyan, Samaxi, Samkir, Samux, Sarur, Siyazan, Susa, Tartar, Tovuz, Ucar, Xacmaz, Xizi, Xocali, Xocavand, Yardimli, Yevlax, Zangilan, Zaqatala, Zardab
cities: Baku, Ganca, Lankaran, Mingacevir, Naftalan, Naxcivan (Nakhichevan), Saki, Sirvan, Sumqayit, Xankandi, Yevlax
Independence
30 August 1991 (declared from the Soviet Union); 18 October 1991 (adopted by the Supreme Council of Azerbaijan)
National holiday
Republic Day (founding of the Democratic Republic of Azerbaijan), 28 May (1918)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 12 November 1995
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or by at least 63 members of the National Assembly; passage requires at least 95 votes of Assembly members in two separate readings of the draft amendment six months apart and requires presidential approval after each of the two Assembly votes, followed by presidential signature; constitutional articles on the authority, sovereignty, and unity of the people cannot be amended; amended 2002, 2009, 2016
Legal system
civil law system
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Ilham ALIYEV (since 31 October 2003); First Vice President Mehriban ALIYEVA (since 21 February 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister Ali ASADOV (since 8 October 2019); First Deputy Prime Minister Yaqub EYYUBOV (since June 2006)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president and confirmed by the National Assembly
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds (if needed) for a 7-year term; a single individual is eligible for unlimited terms; election last held on 11 April 2018 (next to be held in 2025); prime minister and first deputy prime minister appointed by the president and confirmed by the National Assembly; note - a constitutional amendment approved in a September 2016 referendum expanded the presidential term from 5 to 7 years; a separate constitutional amendment approved in the same referendum also introduced the post of first vice-president and additional vice-presidents, who are directly appointed by the president
election results: Ilham ALIYEV reelected president (11 April 2018) in first round; percent of vote - Ilham ALIYEV (YAP) 86%, Zahid ORUJ (independent) 3.1%, other 10.9%
note: OSCE observers noted shortcomings in the election, including a restrictive political environment, limits on fundamental freedoms, a lack of genuine competition, and ballot box stuffing
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Assembly or Milli Mejlis (125 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held early on 9 February 2020 (next to be held in 2025)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - YAP 69, CSP 3, AVP 1, CUP 1, ADMP 1, PDR 1, Great Order 1, National Front Party 1, REAL 1, VP 1, Whole Azerbaijan Popular Front 1, party unknown 1, independent 41; composition - men 103, women 22, percent of women 17.6%
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chairman, vice chairman, and 23 judges in plenum sessions and organized into civil, economic affairs, criminal, and rights violations chambers); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the president and appointed by the Milli Majlis; judges appointed for 10 years; Constitutional Court chairman and deputy chairman appointed by the president; other court judges nominated by the president and appointed by the Milli Majlis to serve single 15-year terms
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal (replaced the Economic Court in 2002); district and municipal courts
Political parties and leaders
Azerbaijan Democratic Enlightenment Party or ADMP [Elshan MASAYEV]
Civic Solidarity Party or VHP [Sabir RUSTAMKHANLI]
Civic Unity Party or CUP [Sabir HAJIYEV]
Great Order Party [Fazil MUSTAFA]
Islamic Party of Azerbaijan or AiP [Mavsum SAMADOV]
Musavat [Arif HAJILI]
Popular Front Party [Ali KARIMLI]
Motherland Party or AVP [Fazail AGAMALI]
National Front Party [Razi NURULLAYEV]
National Revival Movement Party [Faraj GULIYEV]
Party for Democratic Reforms or PDR [Asim MOLLAZADE]
Republican Alternative Party or REAL [Ilgar MAMMADOV]
Social Democratic Party [Ayaz MUTALIBOV]
Social Prosperity Party [Asli KAZIMOVA]
Unity Party or VP [Tahir KARIMLI]
Whole Azerbaijan Popular Front Party [Gudrat HASANGULIYEV]
New Azerbaijan Party (Yeni Azərbaycan Partiyasi) or YAP [Ilham ALIYEV]
International organization participation
ADB, BSEC, CD, CE, CICA, CIS, EAPC, EBRD, ECO, FAO, GCTU, GUAM, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Kahzar IBRAHIM (since 15 September 2021)
chancery: 2741 34th Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 337-3500
FAX: [1] (202) 337-5911
email address and website:
azerbaijan@azembassy.us; consul@azembassy.us
https://washington.mfa.gov.az/en
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Lee LITZENBERGER (since 12 March 2019)
embassy: 111 Azadlig Avenue, AZ1007 Baku
mailing address: 7050 Baku Place, Washington, DC 20521-7050
telephone: [994] (12) 488-3300
FAX: [994] (12) 488-3330
email address and website:
BakuACS@state.gov
https://az.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of sky blue (top), red, and green; a vertical crescent moon and an eight-pointed star in white are centered in the red band; the blue band recalls Azerbaijan's Turkic heritage, red stands for modernization and progress, and green refers to Islam; the crescent moon and star are a Turkic insignia; the eight star points represent the eight Turkic peoples of the world
National symbol(s)
flames of fire; national colors: blue, red, green
National anthem
name: "Azerbaijan Marsi" (March of Azerbaijan)
lyrics/music: Ahmed JAVAD/Uzeyir HAJIBEYOV
note: adopted 1992; although originally written in 1919 during a brief period of independence, "Azerbaijan Marsi" did not become the official anthem until after the dissolution of the Soviet Union
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 3 (all cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Walled City of Baku; Gobustan Rock Art Cultural Landscape; Historic Center of Sheki
Economy
Economic overview
Prior to the decline in global oil prices since 2014, Azerbaijan's high economic growth was attributable to rising energy exports and to some non-export sectors. Oil exports through the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline, the Baku-Novorossiysk, and the Baku-Supsa Pipelines remain the main economic driver, but efforts to boost Azerbaijan's gas production are underway. The expected completion of the geopolitically important Southern Gas Corridor (SGC) between Azerbaijan and Europe will open up another source of revenue from gas exports. First gas to Turkey through the SGC is expected in 2018 with project completion expected by 2020-21.
Declining oil prices caused a 3.1% contraction in GDP in 2016, and a 0.8% decline in 2017, highlighted by a sharp reduction in the construction sector. The economic decline was accompanied by higher inflation, a weakened banking sector, and two sharp currency devaluations in 2015. Azerbaijan’s financial sector continued to struggle. In May 2017, Baku allowed the majority state-owed International Bank of Azerbaijan (IBA), the nation’s largest bank, to default on some of its outstanding debt and file for restructuring in Azerbaijani courts; IBA also filed in US and UK bankruptcy courts to have its restructuring recognized in their respective jurisdictions.
Azerbaijan has made limited progress with market-based economic reforms. Pervasive public and private sector corruption and structural economic inefficiencies remain a drag on long-term growth, particularly in non-energy sectors. The government has, however, made efforts to combat corruption, particularly in customs and government services. Several other obstacles impede Azerbaijan's economic progress, including the need for more foreign investment in the non-energy sector and the continuing conflict with Armenia over the Nagorno-Karabakh region. While trade with Russia and the other former Soviet republics remains important, Azerbaijan has expanded trade with Turkey and Europe and is seeking new markets for non-oil/gas exports - mainly in the agricultural sector - with Gulf Cooperation Council member countries, the US, and others. It is also improving Baku airport and the Caspian Sea port of Alat for use as a regional transportation and logistics hub.
Long-term prospects depend on world oil prices, Azerbaijan's ability to develop export routes for its growing gas production, and its ability to improve the business environment and diversify the economy. In late 2016, the president approved a strategic roadmap for economic reforms that identified key non-energy segments of the economy for development, such as agriculture, logistics, information technology, and tourism. In October 2017, the long-awaited Baku-Tbilisi-Kars railway, stretching from the Azerbaijani capital to Kars in north-eastern Turkey, began limited service.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$138.51 billion (2020 est.)
$144.74 billion (2019 est.)
$141.24 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
0.1% (2017 est.)
-3.1% (2016 est.)
0.6% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$13,700 (2020 est.)
$14,400 (2019 est.)
$14,200 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$48.104 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.6% (2019 est.)
2.3% (2018 est.)
12.8% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: BB+ (2016)
Moody's rating: Ba2 (2017)
Standard & Poors rating: BB+ (2016)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 6.1% (2017 est.)
industry: 53.5% (2017 est.)
services: 40.4% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 57.6% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.5% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 23.6% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.5% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 48.7% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -42% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, wheat, potatoes, barley, tomatoes, watermelons, cotton, apples, maize, onions
Industries
petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, oilfield equipment; steel, iron ore; cement; chemicals and petrochemicals; textiles
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 37%
industry: 14.3%
services: 48.9% (2014)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 12.4%
male: 10.9%
female: 14.2% (2019 est.)
Population below poverty line
4.9% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
33.7 (2008)
36.5 (2001)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3.4%
highest 10%: 27.4% (2008)
Budget
revenues: 9.556 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 10.22 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$1.685 billion (2017 est.)
-$1.363 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$15.21 billion (2020 est.)
$23.63 billion (2019 est.)
$25.48 billion (2018 est.)
note: Data are in current year dollars and do not include illicit exports or re-exports.
Exports - partners
Italy 28%, Turkey 15%, Israel 7%, Germany 5%, India 5% (2017)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, natural gas, refined petroleum, tomatoes, gold (2019)
Imports
$15.54 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$17.71 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$17.71 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - partners
United Kingdom 17%, Russia 17%, Turkey 12%, China 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
gold, cars, refined petroleum, wheat, packaged medical supplies (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$6.681 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$7.142 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$17.41 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$13.83 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Azerbaijani manats (AZN) per US dollar -
1.723 (2017 est.)
1.5957 (2016 est.)
1.5957 (2015 est.)
1.0246 (2014 est.)
0.7844 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 7.677 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 21.027 billion kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 1.491 billion kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 137 million kWh (2020 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.226 billion kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 94.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0.4% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 4.4% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.8% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 19,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 19,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 711,700 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 107,500 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 679,900 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 7 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
138,900 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61Natural gas
production: 23.075 billion cubic meters (2019 est.)
consumption: 11.468 billion cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 11.586 billion cubic meters (2019 est.)
imports: 1.233 billion cubic meters (2019 est.)
proven reserves: 1.699 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
35.389 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 29,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 12.863 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 22.497 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
64.416 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1,652,688 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 16 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 10,344,300 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 102 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: in spite of the telecom sector being one of the major contributors to Azerbaijan’s non-oil GDP, overall development, growth, and investment in the sector has been held back by years of political and civil unrest coupled with endemic corruption; mobile penetration rates reached 100% as far back as 2011 but have largely stagnated since then; the Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are slowly extending the reach of their LTE networks around the country, and this increased coverage (along with access to faster data-based services) is expected to produce a moderate resurgence for both mobile and mobile broadband over the next few years as customers migrate from 3G to 4G. 5G services are still some ways off, as the demand for high-speed data and fast broadband can easily be met by existing capacity on LTE networks; fixed-line teledensity continues to drop down each year as customers consolidate their telecommunications services around the mobile platform; the rate of decline is comparatively slower than other countries, since Azerbaijan has a relatively high proportion of (87%) of fixed-line broadband customers still on DSL; fiber is gradually being rolled out in urban areas, and this makes up the bulk of the growth being seen in the overall fixed broadband market; DSL’s predominance, however, will serve to keep Azerbaijan’s average access speeds in the sub-10Mbps range for the foreseeable future (2020)
domestic: teledensity of some 16 fixed-lines per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity of 102 telephones per 100 persons; satellite service connects Baku to a modern switch in its exclave of Naxcivan (Nakhchivan) (2020)
international: country code - 994; the TAE fiber-optic link transits Azerbaijan providing international connectivity to neighboring countries; the old Soviet system of cable and microwave is still serviceable; satellite earth stations - 2 (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
3 state-run and 1 public TV channels; 4 domestic commercial TV stations and about 15 regional TV stations; cable TV services are available in Baku; 1 state-run and 1 public radio network operating; a small number of private commercial radio stations broadcasting; local FM relays of Baku commercial stations are available in many localities; note - all broadcast media is pro-government, and most private broadcast media outlets are owned by entities directly linked to the government
Internet users
total: 8,745,304 (2022 est.)
percent of population: 85% (2022 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1,995,474 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 20 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 42 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 44
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 2,279,546 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 44.09 million (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
total: 30
over 3,047 m: 5
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 13
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 3 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 7
under 914 m: 7 (2021)
Heliports
1 (2021)
Pipelines
89 km condensate, 3,890 km gas, 2,446 km oil (2013)
Railways
total: 2,944.3 km (2017)
broad gauge: 2,944.3 km (2017) 1.520-m gauge (approx. 1,767 km electrified)
Roadways
total: 24,981 km (2013)
note: total roadway length has increased significantly and continues to grow due to the recovery of Armenian-held territories and related reconstruction efforts. No updated figure is currently available.
Merchant marine
total: 305
by type: general cargo 38, oil tanker 43, other 224 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Baku (Baki) located on the Caspian Sea
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Azerbaijan Armed Forces: Land Forces (Combined Arms Army), Air Forces, Navy Forces; Ministry of Internal Affairs: State Border Service (includes Coast Guard), Internal Security Troops (2022)
Military expenditures
5.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
5.4% of GDP (2020 est.)
3.8% of GDP (2019 est.) (approximately $3.4 billion)
3.6% of GDP (2018 est.) (approximately $3.2 billion)
3.8% of GDP (2017 est.) (approximately $3.26 billion)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 65,000 active armed forces (55,000 Army; 2,000 Navy; 8,000 Air Force); approximately 15,000 Ministry of Internal Affairs troops (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory is comprised mostly of Russian and Soviet-era weapons systems with a small mix of equipment from other countries, including Israel and Turkey (2022)
Military service age and obligation
18-35 years of age for compulsory military service for men; 17-35 years of age for voluntary service for men and women (2022)
note: as of 2018, women made up an estimated 3% of the active duty military
Military - note
since November 2020, Russia has deployed about 2,000 peacekeeping troops to the area in and around Nagorno-Karabakh as part of a cease-fire agreement between Armenia and Azerbaijan; fighting erupted between the two countries over the Nagorno-Karabakh region in September of 2020; Nagorno-Karabakh lies within Azerbaijan but has been under control of ethnic Armenian forces (the "Nagorno-Karabakh Defense Army") backed by Armenia since a separatist war there ended in 1994; six weeks of fighting resulted in about 6,500 deaths and ended after Armenia ceded swaths of Nagorno-Karabakh territory; tensions remained high in 2022, and both sides have accused the other of provocations since the fighting ended; Armenia has accused Azerbaijani forces of a series of border intrusions and of seizing pockets of territory
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS); Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)/Qods Force
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Local border forces struggle to control the illegal transit of goods and people across the porous, undemarcated Armenian, Azerbaijani, and Georgian borders.
Armenia-Azerbaijan: The dispute over the break-away Nagorno-Karabakh region and the Armenian military occupation of surrounding lands in Azerbaijan remains the primary focus of regional instability. Residents have evacuated the former Soviet-era small ethnic enclaves in Armenia and Azerbaijan.
Azerbaijan-Georgia: A joint boundary commission agrees on most of the alignment, leaving only small areas at certain crossing points in dispute. Consequently, the two states have yet to agree on a delimitation or demarcation of their common boundary. One area of contention is where the international boundary should run through the 6th-13th Century David-Gareja monastery complex.
Azerbaijan-Iran: none identified
Azerbaijan-Russia: Russia complains of cross-border smuggling.
Azerbaijan-Turkey: none identified
Caspian Sea (Maritime Boundary): Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Russia ratified the Caspian seabed delimitation treaties based on equidistance, while Iran continues to insist on a one-fifth slice of the sea. Bilateral talks continue with Turkmenistan on dividing the seabed and contested oilfields in the middle of the Caspian.
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 655,000 (conflict with Armenia over Nagorno-Karabakh; IDPs are mainly ethnic Azerbaijanis but also include ethnic Kurds, Russians, and Turks predominantly from occupied territories around Nagorno-Karabakh; includes IDPs' descendants, returned IDPs, and people living in insecure areas and excludes people displaced by natural disasters; around half the IDPs live in the capital Baku) (2021)
stateless persons: 3,585 (mid-year 2021)
Illicit drugs
limited illicit cultivation of cannabis and opium poppy, mostly for CIS consumption; small government eradication program; transit point for Southwest Asian opiates bound for Russia and to a lesser extent the rest of Europe