Introduction
Background
The Maya civilization flourished in Guatemala and surrounding regions during the first millennium A.D. After almost three centuries as a Spanish colony, Guatemala won its independence in 1821. During the second half of the 20th century, it experienced a variety of military and civilian governments, as well as a 36-year guerrilla war. In 1996, the government signed a peace agreement formally ending the internal conflict.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Central America, bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between El Salvador and Mexico, and bordering the Gulf of Honduras (Caribbean Sea) between Honduras and Belize
Geographic coordinates
15 30 N, 90 15 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Land boundaries
total: 1,667 km
border countries (4): Belize 266 km; El Salvador 199 km; Honduras 244 km; Mexico 958 km
Coastline
400 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate
tropical; hot, humid in lowlands; cooler in highlands
Terrain
two east-west trending mountain chains divide the country into three regions: the mountainous highlands, the Pacific coast south of mountains, and the vast northern Peten lowlands
Elevation
highest point: Volcan Tajumulco (highest point in Central America) 4,220 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 759 m
Natural resources
petroleum, nickel, rare woods, fish, chicle, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 41.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 14.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 8.8% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 18.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 33.6% (2018 est.)
other: 25.2% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
3,375 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
fresh water lake(s): Lago de Izabal - 590 sq km
Population distribution
the vast majority of the populace resides in the southern half of the country, particularly in the mountainous regions; more than half of the population lives in rural areas
Natural hazards
numerous volcanoes in mountains, with occasional violent earthquakes; Caribbean coast extremely susceptible to hurricanes and other tropical storms
volcanism: significant volcanic activity in the Sierra Madre range; Santa Maria (3,772 m) has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Pacaya (2,552 m), which erupted in May 2010 causing an ashfall on Guatemala City and prompting evacuations, is one of the country's most active volcanoes with frequent eruptions since 1965; other historically active volcanoes include Acatenango, Almolonga, Atitlan, Fuego, and Tacana; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Geography - note
note 1: despite having both eastern and western coastlines (Caribbean Sea and Pacific Ocean respectively), there are no natural harbors on the west coast
note 2: Guatemala is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Guatemalan(s)
adjective: Guatemalan
Ethnic groups
Mestizo (mixed Amerindian-Spanish - in local Spanish called Ladino) 56%, Maya 41.7%, Xinca (Indigenous, non-Maya) 1.8%, African descent 0.2%, Garifuna (mixed West and Central African, Island Carib, and Arawak) 0.1%, foreign 0.2% (2018 est.)
Languages
Spanish (official) 69.9%, Maya languages 29.7% (Q'eqchi' 8.3%, K'iche 7.8%, Mam 4.4%, Kaqchikel 3%, Q'anjob'al 1.2%, Poqomchi' 1%, other 4%), other 0.4% (includes Xinca and Garifuna); note - the 2003 Law of National Languages officially recognized 23 indigenous languages, including 21 Maya languages, Xinca, and Garifuna (2018 est.)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 41.7%, Evangelical 38.8%, other 2.7%, atheist 0.1%, none 13.8%, unspecified 2.9% (2018 est.)
Demographic profile
Guatemala is a predominantly poor country that struggles in several areas of health and development, including infant, child, and maternal mortality, malnutrition, literacy, and contraceptive awareness and use. The country's large indigenous population is disproportionately affected. Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and has the highest fertility rate in Latin America. It also has the highest population growth rate in Latin America, which is likely to continue because of its large reproductive-age population and high birth rate. Almost half of Guatemala's population is under age 19, making it the youngest population in Latin America. Guatemala's total fertility rate has slowly declined during the last few decades due in part to limited government-funded health programs. However, the birth rate is still more close to three children per woman and is markedly higher among its rural and indigenous populations.
Guatemalans have a history of emigrating legally and illegally to Mexico, the United States, and Canada because of a lack of economic opportunity, political instability, and natural disasters. Emigration, primarily to the United States, escalated during the 1960 to 1996 civil war and accelerated after a peace agreement was signed. Thousands of Guatemalans who fled to Mexico returned after the war, but labor migration to southern Mexico continues.
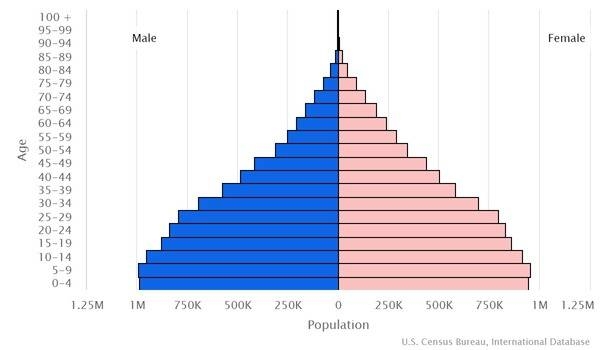
Age structure
0-14 years: 33.68% (male 2,944,145/female 2,833,432)
15-24 years: 19.76% (male 1,705,730/female 1,683,546)
25-54 years: 36.45% (male 3,065,933/female 3,186,816)
55-64 years: 5.41% (male 431,417/female 496,743)
65 years and over: 4.7% (male 363,460/female 442,066) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 60.9
youth dependency ratio: 53
elderly dependency ratio: 7.9
potential support ratio: 12.7 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 23.2 years
male: 22.6 years
female: 23.8 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the vast majority of the populace resides in the southern half of the country, particularly in the mountainous regions; more than half of the population lives in rural areas
Urbanization
urban population: 53.1% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.59% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.095 million GUATEMALA CITY (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.68 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.6 years (2014/15 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
95 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72Infant mortality rate
total: 26.18 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 29.51 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 22.69 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 72.91 years
male: 70.88 years
female: 75.04 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
60.6% (2014/15)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 97.9% of population
rural: 92.2% of population
total: 95% of population
unimproved: urban: 2.1% of population
rural: 8% of population
total: 5% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
6.2% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
1.24 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
Hospital bed density
0.4 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 90.4% of population
rural: 66.3% of population
total: 78.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 9.6% of population
rural: 33.7% of population
total: 21.2% of population (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 1.63 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.9 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.05 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.68 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 10.9% (2020 est.)
male: 20.1% (2020 est.)
female: 1.6% (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 80.8%
male: 85.3%
female: 76.7% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 11 years
male: 11 years
female: 10 years (2019)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 4.6%
male: 4%
female: 5.7% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation in the Peten rainforest; soil erosion; water pollution
Environment - international agreements
party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 23.59 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 16.78 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 10.7 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; hot, humid in lowlands; cooler in highlands
Land use
agricultural land: 41.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 14.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 8.8% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 18.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 33.6% (2018 est.)
other: 25.2% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 53.1% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.59% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.78% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2,756,741 tons (2015 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
fresh water lake(s): Lago de Izabal - 590 sq km
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 835 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 603.1 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 1.886 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
127.91 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Guatemala
conventional short form: Guatemala
local long form: Republica de Guatemala
local short form: Guatemala
etymology: the Spanish conquistadors used many native Americans as allies in their conquest of Guatemala; the site of their first capital (established in 1524), a former Maya settlement, was called "Quauhtemallan" by their Nahuatl-speaking Mexican allies, a name that means "land of trees" or "forested land", but which the Spanish pronounced "Guatemala"; the Spanish applied that name to a re-founded capital city three years later and eventually it became the name of the country
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Guatemala City
geographic coordinates: 14 37 N, 90 31 W
time difference: UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the Spanish conquistadors used many native Americans as allies in their conquest of Guatemala; the site of their first capital (established in 1524), a former Maya settlement, was called "Quauhtemallan" by their Nahuatl-speaking Mexican allies, a name that means "land of trees" or "forested land", but which the Spanish pronounced "Guatemala"; the Spanish applied that name to a re-founded capital city three years later and eventually it became the name of the country
Administrative divisions
22 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Alta Verapaz, Baja Verapaz, Chimaltenango, Chiquimula, El Progreso, Escuintla, Guatemala, Huehuetenango, Izabal, Jalapa, Jutiapa, Peten, Quetzaltenango, Quiche, Retalhuleu, Sacatepequez, San Marcos, Santa Rosa, Solola, Suchitepequez, Totonicapan, Zacapa
Independence
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
National holiday
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 31 May 1985, effective 14 January 1986; suspended and reinstated in 1994
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic, by agreement of 10 or more deputies of Congress, by the Constitutional Court, or by public petition of at least 5,000 citizens; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Congress membership and approval by public referendum, referred to as "popular consultation"; constitutional articles such as national sovereignty, the republican form of government, limitations on those seeking the presidency, or presidential tenure cannot be amended; amended 1993
Legal system
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years with no absences of six consecutive months or longer or absences totaling more than a year
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal; note - active duty members of the armed forces and police by law cannot vote and are restricted to their barracks on election day
Executive branch
chief of state: President Alejandro GIAMMATTEI (since 14 January 2020); Vice President Cesar Guillermo CASTILLO Reyes (since 14 January 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Alejandro GIAMMATTEI (since 14 January 2020); Vice President Cesar Guillermo CASTILLO Reyes (since 14 January 2020)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (not eligible for consecutive terms); election last held on 16 June 2019 with a runoff on 11 August 2019 (next to be held in June 2023)
election results:
2019: Alejandro GIAMMATTEI elected president; percent of vote in first round - Sandra TORRES (UNE) 25.5%, Alejandro GIAMMATTEI (VAMOS) 14%, Edmond MULET (PHG) 11.2%, Thelma CABRERA (MLP) 10.4%, Roberto ARZU (PAN-PODEMOS) 6.1%, other 32.8%; percent of vote in second round - Alejandro GIAMMATTEI (VAMOS) 58%, Sandra TORRES (UNE) 42%
2015: Jimmy Ernesto MORALES Cabrera elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Jimmy Ernesto MORALES Cabrera (FNC) 23.9%, Sandra TORRES (UNE) 19.8%, Manuel BALDIZON (LIDER) 19.6%, other 36.7%; percent of vote in second round - Jimmy Ernesto MORALES Cabrera 67.4%, Sandra TORRES 32.6%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Congress of the Republic or Congreso de la Republica (160 seats; 128 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies in the country's 22 departments and 32 directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by closed party-list proportional representation vote, using the D'Hondt method; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 16 June 2019 (next to be held on June 2023)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - UNE 52, VAMOS 17, UCN 12, VALOR 9, BIEN 8, FCN-NACION 8, SEMILLA 7, TODOS 7, VIVA 7, CREO 6, PHG 6, VICTORIA 4, Winaq 4, PC 3, PU 3, URNG 3, PAN 2, MLP 1, PODEMOS 1; composition - men 129, women 31, percent of women 19.4%
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Justice or Corte Suprema de Justicia (consists of 13 magistrates, including the court president and organized into 3 chambers); note - the court president also supervises trial judges countrywide; note - the Constitutional Court or Corte de Constitucionalidad of Guatemala resides outside the country's judicial system; its sole purpose is the interpretation of the constitution and to see that the laws and regulations are not superior to the constitution (consists of 5 titular magistrates and 5 substitute magistrates)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court magistrates elected by the Congress of the Republic from candidates proposed by the Postulation Committee, an independent body of deans of the country's university law schools, representatives of the country's law associations, and representatives of the Courts of Appeal; magistrates elected for concurrent, renewable 5-year terms; Constitutional Court judges - 1 elected by the Congress of the Republic, 1 by the Supreme Court, 1 by the president of the republic, 1 by the (public) University of San Carlos, and 1 by the Assembly of the College of Attorneys and Notaries; judges elected for renewable, consecutive 5-year terms; the presidency of the court rotates among the magistrates for a single 1-year term
subordinate courts: Appellate Courts of Accounts, Contentious Administrative Tribunal, courts of appeal, first instance courts, child and adolescence courts, minor or peace courts
Political parties and leaders
Bienestar Nacional or BIEN [Fidel REYES LEE]
Citizen Prosperity or PC [Hernan MEJIA and Jorge GARCIA SILVA]
Commitment, Renewal, and Order or CREO [Rodolfo NEUTZE]
Everyone Together for Guatemala or TODOS [Felipe ALEJOS]
Guatemalan National Revolutionary Unity or URNG-MAIZ or URNG [Walter FELIX]
Humanist Party of Guatemala or PHG [Rudio MERIDA]
Movement for the Liberation of Peoples or MLP [Thelma CABRERA and Vincenta JERONIMO]
Movimiento Semilla or SEMILLA [Samuel PEREZ Alvarez]
National Advancement Party or PAN [Manuel CONDE]
National Convergence Front or FCN-NACION [Javier HERNANDEZ]
National Unity for Hope or UNE [Sandra TORRES and Jorge VARGAS]
Nationalist Change Union or UCN [Carlos ROJAS and Sofia HERNANDEZ] (dissolved 16 December 2021)
PODEMOS [Jose LEON]
Political Movement Winaq or Winaq [Sonia GUTIERREZ Raguay]
Value or VALOR [Zury RIOS and Lucrecia MARROQUIN]
Vamos por una Guatemala Diferente or VAMOS [Alejandro GIAMMATTEI]
Victory or VICTORIA [Abraham RIVERA and his four sons Amilcar, Juan, Manuel, and Edgar]
Vision with Values or VIVA [Armando Damian CASTILLO Alvarado]
International organization participation
BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNITAR, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Alfonso Jose QUINONEZ LEMUS (since 17 July 2020)
chancery: 2220 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 745-4953
FAX: [1] (202) 745-1908
email address and website:
infoembaguateeuu@minex.gob.gt
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Chicago, Del Rio (TX), Denver, Houston, Los Angeles, McAllen (TX), Miami, New York, Oklahoma City, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Providence (RI), Raleigh (NC), San Bernardino (CA), San Francisco, Seattle
consulate(s): Lake Worth (FL), Silver Spring (MD), Tucson (AZ)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador William W. POPP (since 13 August 2020)
embassy: Avenida Reforma 7-01, Zone 10, Guatemala City
mailing address: 3190 Guatemala Place, Washington DC 20521-3190
telephone: [502] 2326-4000
FAX: [502] 2326-4654
email address and website:
AmCitsGuatemala@state.gov
https://gt.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal vertical bands of light blue (hoist side), white, and light blue, with the coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms includes a green and red quetzal (the national bird) representing liberty and a scroll bearing the inscription LIBERTAD 15 DE SEPTIEMBRE DE 1821 (the original date of independence from Spain) all superimposed on a pair of crossed rifles signifying Guatemala's willingness to defend itself and a pair of crossed swords representing honor and framed by a laurel wreath symbolizing victory; the blue bands represent the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea; the white band denotes peace and purity
note: one of only two national flags featuring a firearm, the other is Mozambique
National symbol(s)
quetzal (bird); national colors: blue, white
National anthem
name: "Himno Nacional de Guatemala" (National Anthem of Guatemala)
lyrics/music: Jose Joaquin PALMA/Rafael Alvarez OVALLE
note: adopted 1897, modified lyrics adopted 1934; Cuban poet Jose Joaquin PALMA anonymously submitted lyrics to a public contest calling for a national anthem; his authorship was not discovered until 1911
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 3 (2 cultural, 1 mixed)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Antigua Guatemala (c); Tikal National Park (m); Archaeological Park and Ruins of Quirigua (c)
Economy
Economic overview
Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America with a GDP per capita roughly half the average for Latin America and the Caribbean. The agricultural sector accounts for 13.5% of GDP and 31% of the labor force; key agricultural exports include sugar, coffee, bananas, and vegetables. Guatemala is the top remittance recipient in Central America as a result of Guatemala's large expatriate community in the US. These inflows are a primary source of foreign income, equivalent to two-thirds of the country's exports and about a tenth of its GDP.
The 1996 peace accords, which ended 36 years of civil war, removed a major obstacle to foreign investment, and Guatemala has since pursued important reforms and macroeconomic stabilization. The Dominican Republic-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) entered into force in July 2006, spurring increased investment and diversification of exports, with the largest increases in ethanol and non-traditional agricultural exports. While CAFTA-DR has helped improve the investment climate, concerns over security, the lack of skilled workers, and poor infrastructure continue to hamper foreign direct investment.
The distribution of income remains highly unequal with the richest 20% of the population accounting for more than 51% of Guatemala's overall consumption. More than half of the population is below the national poverty line, and 23% of the population lives in extreme poverty. Poverty among indigenous groups, which make up more than 40% of the population, averages 79%, with 40% of the indigenous population living in extreme poverty. Nearly one-half of Guatemala's children under age five are chronically malnourished, one of the highest malnutrition rates in the world.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$141.5 billion (2020 est.)
$143.68 billion (2019 est.)
$138.33 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.8% (2017 est.)
3.1% (2016 est.)
4.1% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$8,400 (2020 est.)
$8,700 (2019 est.)
$8,500 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$76.678 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
3.7% (2019 est.)
3.7% (2018 est.)
4.4% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: BB- (2020)
Moody's rating: Ba1 (2010)
Standard & Poors rating: BB- (2017)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 13.3% (2017 est.)
industry: 23.4% (2017 est.)
services: 63.2% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 86.3% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 9.7% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 12.3% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -0.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 18.8% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -26.9% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, bananas, oil palm fruit, maize, melons, potatoes, milk, plantains, pineapples, rubber
Industries
sugar, textiles and clothing, furniture, chemicals, petroleum, metals, rubber, tourism
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 31.4%
industry: 12.8%
services: 55.8% (2017 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 4.6%
male: 4%
female: 5.7% (2019 est.)
Population below poverty line
59.3% (2014 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
48.3 (2014 est.)
56 (2011)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.6%
highest 10%: 38.4% (2014)
Budget
revenues: 8.164 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 9.156 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$1.134 billion (2017 est.)
$1.023 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$13.12 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$13.6 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$13.35 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - partners
United States 33%, El Salvador 12%, Honduras 8%, Mexico 5%, Nicaragua 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
bananas, raw sugar, coffee, cardamom, palm oil (2019)
Imports
$19.3 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$21.52 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$21.17 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - partners
United States 36%, China 12%, Mexico 11%, El Salvador 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, packaged medicines, cars, delivery trucks (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$11.77 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$9.156 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$22.92 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$21.45 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
quetzales (GTQ) per US dollar -
7.323 (2017 est.)
7.5999 (2016 est.)
7.5999 (2015 est.)
7.6548 (2014 est.)
7.7322 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 92% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 99% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 85% (2019)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 5.185 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 10,793,650,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 2.19 billion kWh (2019 est.)
imports: 1.141 billion kWh (2019 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.587 billion kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 39.4% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 1.5% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 2.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 38% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 2.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 17% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 2.28 million metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 2.376 million metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 10,300 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 112,600 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 6,700 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 86.1 million barrels (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
1,162 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105Natural gas
production: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
19.041 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 5.037 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 14.004 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
19.411 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 2,272,467 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 13 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 20,390,671 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 114 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Guatemala’s telecom infrastructure has suffered from years of under investment from state and provincial government; the poor state of fixed-line infrastructure has led to Guatemala having one of the lowest fixed-line teledensities in the region; in many rural regions of the country there is no fixed-line access available, and so mobile services are adopted by necessity; private investment has been supported by government and regulatory efforts, resulting in a steady growth in the number of fixed lines which has supported growth in the fixed broadband segment; delays in launching LTE services left the country lagging behind in the development of mobile broadband and the benefits which it can bring to the country's social and economic growth; two new submarine cables are due for completion by 2022; improved international connectivity should drive further uptake of both fixed and mobile broadband services; intense competition among the networks has helped to improve services and lower prices for end-users; given the commercial impetus of networks, insufficient government financial investment has resulted in many regional areas remaining with poor or non-existent services; the country benefits from one of the most open regulatory frameworks, with all telecom sectors having been open to competition since 1996; mobile subscriptions are on par with the regional average, though the slower growth in the mobile subscriber base suggests a level of market saturation, with the emphasis among networks being on generating revenue via mobile data services (2021)
domestic: fixed-line teledensity roughly 13 per 100 persons; fixed-line investments are concentrating on improving rural connectivity; mobile-cellular teledensity about 114 per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 502; landing points for the ARCOS, AMX-1, American Movil-Texius West Coast Cable and the SAm-1 fiber-optic submarine cable system that, together, provide connectivity to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; connected to Central American Microwave System; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
4 privately owned national terrestrial TV channels dominate TV broadcasting; multi-channel satellite and cable services are available; 1 government-owned radio station and hundreds of privately owned radio stations (2019)
Internet users
total: 8,429,167 (2020 est.)
percent of population: 50% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 612,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 3 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 5
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 145,795 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 110,000 (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
total: 16
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 6
under 914 m: 4 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 275
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 77
under 914 m: 195 (2021)
Heliports
1 (2021)
Pipelines
480 km oil (2013)
Railways
total: 800 km (2018)
narrow gauge: 800 km (2018) 0.914-m gauge
note: despite the existence of a railway network, all rail service was suspended in 2007 and no passenger or freight train currently runs in the country (2018)
Roadways
total: 17,440 km (2020)
paved: 7,458 km (2020)
unpaved: 9,982 km (2020) (includes 4,548 km of rural roads)
Waterways
990 km (2012) (260 km navigable year round; additional 730 km navigable during high-water season)
country comparison to the world: 71Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Puerto Quetzal, Santo Tomas de Castilla
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Army of Guatemala (Ejercito de Guatemala): Land Forces (Fuerzas de Tierra), Naval Forces (Fuerzas de Mar), and Air Force (Fuerza de Aire); Ministry of Government (Interior): National Civil Police (Policia Nacional Civil; includes paramilitary units) (2022)
Military expenditures
0.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.4% of GDP (2021)
0.4% of GDP (2020)
0.4% of GDP (2019) (approximately $530 million)
0.4% of GDP (2018) (approximately $470 million)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 20,000 active military personnel (18,000 Land Forces; 1,000 Naval Forces; 1,000 Air Forces); approximately 30,000 National Civil Police (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Guatemalan military inventory is small and mostly comprised of older US equipment; since 2010, Guatemala has received small amounts of equipment from several countries, including the US (2022)
Military service age and obligation
all male citizens between the ages of 18 and 50 are eligible for military service; in practice, most of the force is volunteer, however, a selective draft system is employed, resulting in a small portion of 17-21 year-olds being conscripted; conscript service obligation varies from 1 to 2 years; women may volunteer (2022)
note: as of 2017, women comprised up to 10% of the active military
Military deployments
155 Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO) (May 2022)
Military - note
since the 2000s, the Guatemalan Government has used the Army to support the National Civil Police in internal security operations (as permitted by the constitution) to combat organized crime, gang violence, and narco-trafficking
the military held power during most of Guatemala’s 36-year civil war (1960-1996) and conducted a campaign of widespread violence and repression, particularly against the country’s majority indigenous population; more than 200,000 people were estimated to have been killed or disappeared during the conflict (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Guatemala-Belize: Demarcated but insecure boundary due to Guatemala’s claims to more than half of Belizean territory. Line of Adjacency operates in lieu of an international boundary to control influx of Guatemalan squatters onto Belizean territory. Smuggling, narcotics trafficking, and human trafficking for sexual exploitation and debt bondage are all problems. Belize lacks resources to detect and extradite impoverished Guatemalan peasants squatting in Belizean rain forests in the remote border areas. Both countries agreed in April 2012 to hold simultaneous referenda, scheduled for 6 October 2013, to decide whether to refer the dispute to the ICJ for binding resolution, but this vote was suspended indefinitely. At present, Belize and Honduras 12-nm territorial sea claims close off Guatemalan access to Caribbean in the Bahia de Amatique. Maritime boundary remains unresolved pending further negotiation.
Guatemala-Mexico: Mexico must deal with thousands of impoverished Guatemalans and other Central Americans who cross the porous border looking for work in Mexico and the US.
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 243,000 (more than three decades of internal conflict that ended in 1996 displaced mainly the indigenous Maya population and rural peasants; ongoing drug cartel and gang violence) (2021)
Illicit drugs
a major transit country for illegal drugs destined for the United States with increasing cultivation originating from Guatemala; farmers cultivate opium poppy and cannabis