Introduction
Background
Berbers have inhabited central north Africa since ancient times, but the region has been settled and ruled by Phoenicians, Greeks, Carthaginians, Persians, Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, and Vandals. In the the 7th century, Islam spread through the region; in the mid-16th century, Ottoman rule began. The Italians supplanted the Ottoman Turks in the area around Tripoli in 1911 and did not relinquish their hold until 1943 when they were defeated in World War II. Libya then passed to UN administration and achieved independence in 1951. Following a 1969 military coup, Col. Muammar al-QADHAFI assumed leadership and began to espouse his political system at home, which was a combination of socialism and Islam. During the 1970s, QADHAFI used oil revenues to promote his ideology outside Libya, supporting subversive and terrorist activities that included the downing of two airliners - one over Scotland, another in Northern Africa - and a discotheque bombing in Berlin. UN sanctions in 1992 isolated QADHAFI politically and economically following the attacks; sanctions were lifted in 2003 following Libyan acceptance of responsibility for the bombings and agreement to claimant compensation. QADHAFI also agreed to end Libya's program to develop weapons of mass destruction, and he made significant strides in normalizing relations with Western nations.
Unrest that began in several Middle Eastern and North African countries in late 2010 erupted in Libyan cities in early 2011. QADHAFI's brutal crackdown on protesters spawned an eight-month civil war that saw UN authorization of air and naval intervention by the international community, the toppling of the QADHAFI regime, and the setting up of a National Transitional Council (NTC). In 2012, the NTC handed power to an elected parliament, the General National Congress (GNC). Voters chose a new parliament to replace the GNC in June 2014 - the House of Representatives (HoR), which relocated to the eastern city of Tobruk after fighting broke out in Tripoli and Benghazi in July 2014.
In December 2015, the UN brokered an agreement among a broad array of Libyan political parties and social groups - known as the Libyan Political Agreement (LPA). Members of the Libyan Political Dialogue signed the LPA in December 2015. In January 2016, The HoR and defunct-GNC-affiliated political hardliners continued to oppose the GNA and hamper the LPA’s implementation. In September 2017, UN Special Representative Ghassan SALAME announced a new roadmap for national political reconciliation. In November 2018, the international partners supported SALAME’s recalibrated Action Plan for Libya that aimed to break the political deadlock by holding a National Conference, subsequently held in early 2019, but attendees failed to reach an agreement. Despite continued clashes since then, the warring parties agreed to a UN-administered ceasefire in October 2020. In early 2021, the UN-led Libyan Political Dialogue Forum selected an interim president and prime minister of its executive council. The council was charged with preparing for December 2021 presidential and parliamentary elections.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
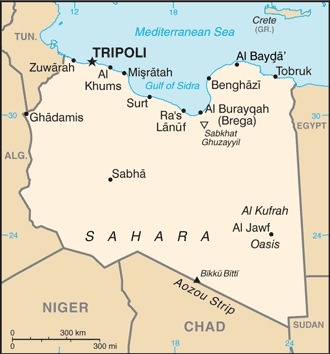
Location
Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt, Tunisia, and Algeria
Geographic coordinates
25 00 N, 17 00 E
Map references
Africa
Land boundaries
total: 4,339 km
border countries (6): Algeria 989 km, Chad 1050 km, Egypt 1115 km, Niger 342 km, Sudan 382 km, Tunisia 461 km
Coastline
1,770 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive fishing zone: 62 nm
note: Gulf of Sidra closing line - 32 degrees, 30 minutes north
Climate
Mediterranean along coast; dry, extreme desert interior
Terrain
mostly barren, flat to undulating plains, plateaus, depressions
Elevation
highest point: Bikku Bitti 2,267 m
lowest point: Sabkhat Ghuzayyil -47 m
mean elevation: 423 m
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, gypsum
Land use
agricultural land: 8.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 7.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.1% (2018 est.)
other: 91.1% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
4,700 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km)
Major aquifers
Nubian Aquifer System, North Western Sahara Aquifer System, Murzuk-Djado Basin
Population distribution
well over 90% of the population lives along the Mediterranean coast in and between Tripoli to the west and Al Bayda to the east; the interior remains vastly underpopulated due to the Sahara and lack of surface water as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
hot, dry, dust-laden ghibli is a southern wind lasting one to four days in spring and fall; dust storms, sandstorms
Geography - note
note 1: more than 90% of the country is desert or semidesert
note 2: the volcano Waw an Namus lies in south central Libya in the middle of the Sahara; the caldera is an oasis - the name means "oasis of mosquitoes" - containing several small lakes surrounded by vegetation and hosting various insects and a large diversity of birds
People and Society
Population
7,017,224 (July 2021 est.)
note: immigrants make up just over 12% of the total population, according to UN data (2019)
Nationality
noun: Libyan(s)
adjective: Libyan
Ethnic groups
Berber and Arab 97%, other 3% (includes Egyptian, Greek, Indian, Italian, Maltese, Pakistani, Tunisian, and Turkish)
Languages
Arabic (official), Italian, English (all widely understood in the major cities); Berber (Nafusi, Ghadamis, Suknah, Awjilah, Tamasheq)
major-language sample(s):
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim (official; virtually all Sunni) 96.6%, Christian 2.7%, Buddhist <1%, Hindu <1%, Jewish <1%, folk religion <1%, other <1%, unafilliated <1% (2020 est.)
note: non-Sunni Muslims include native Ibadhi Muslims (<1% of the population) and foreign Muslims
Demographic profile
Despite continuing unrest, Libya remains a destination country for economic migrants. It is also a hub for transit migration to Europe because of its proximity to southern Europe and its lax border controls. Labor migrants have been drawn to Libya since the development of its oil sector in the 1960s. Until the latter part of the 1990s, most migrants to Libya were Arab (primarily Egyptians and Sudanese). However, international isolation stemming from Libya’s involvement in international terrorism and a perceived lack of support from Arab countries led QADHAFI in 1998 to adopt a decade-long pan-African policy that enabled large numbers of Sub-Saharan migrants to enter Libya without visas to work in the construction and agricultural industries. Although Sub-Saharan Africans provided a cheap labor source, they were poorly treated and were subjected to periodic mass expulsions.
By the mid-2000s, domestic animosity toward African migrants and a desire to reintegrate into the international community motivated QADHAFI to impose entry visas on Arab and African immigrants and to agree to joint maritime patrols and migrant repatriations with Italy, the main recipient of illegal migrants departing Libya. As his regime neared collapse in 2011, QADHAFI reversed his policy of cooperating with Italy to curb illegal migration and sent boats loaded with migrants and asylum seekers to strain European resources. Libya’s 2011 revolution decreased immigration drastically and prompted nearly 800,000 migrants to flee to third countries, mainly Tunisia and Egypt, or to their countries of origin. The inflow of migrants declined in 2012 but returned to normal levels by 2013, despite continued hostility toward Sub-Saharan Africans and a less-inviting job market.
While Libya is not an appealing destination for migrants, since 2014, transiting migrants – primarily from East and West Africa – continue to exploit its political instability and weak border controls and use it as a primary departure area to migrate across the central Mediterranean to Europe in growing numbers. In addition, more than 200,000 people were displaced internally as of August 2017 by fighting between armed groups in eastern and western Libya and, to a lesser extent, by inter-tribal clashes in the country’s south.
Age structure
0-14 years: 33.65% (male 1,184,755/female 1,134,084)
15-24 years: 15.21% (male 534,245/female 513,728)
25-54 years: 41.57% (male 1,491,461/female 1,373,086)
55-64 years: 5.52% (male 186,913/female 193,560)
65 years and over: 4.04% (male 129,177/female 149,526) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 47.7
youth dependency ratio: 41
elderly dependency ratio: 6.7
potential support ratio: 15 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 25.8 years
male: 25.9 years
female: 25.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
well over 90% of the population lives along the Mediterranean coast in and between Tripoli to the west and Al Bayda to the east; the interior remains vastly underpopulated due to the Sahara and lack of surface water as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 81% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.45% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.170 million TRIPOLI (capital), 919,000 Misratah, 836,000 Benghazi (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
72 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81Infant mortality rate
total: 11.48 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 12.97 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 9.93 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 76.93 years
male: 74.68 years
female: 79.29 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
27.7% (2014)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 98.5% of population
unimproved: total: 1.5% of population (2017 est.)
Physicians density
2.09 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Hospital bed density
3.2 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<100 (2020)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 91%
male: 96.7%
female: 85.6% (2015)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 48.7%
male: 40.8%
female: 67.8% (2012 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
desertification; limited natural freshwater resources; the Great Manmade River Project, the largest water development scheme in the world, brings water from large aquifers under the Sahara to coastal cities; water pollution is a significant problem; the combined impact of sewage, oil byproducts, and industrial waste threatens Libya's coast and the Mediterranean Sea
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Law of the Sea
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 44.17 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 50.56 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 45.76 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
Mediterranean along coast; dry, extreme desert interior
Land use
agricultural land: 8.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 7.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.1% (2018 est.)
other: 91.1% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 81% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.45% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.06% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125Food insecurity
severe localized food insecurity: due to civil insecurity, economic and political instability, and high food prices - an estimated 1.3 million people (23% of the population) are in need of humanitarian assistance of which 700,000 require food assistance; half of the people in need of humanitarian assistance are internally displaced or migrants that are residing in, or transiting through, the country (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2,147,596 tons (2011 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km)
Major aquifers
Nubian Aquifer System, North Western Sahara Aquifer System, Murzuk-Djado Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 700 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 280 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 4.85 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
700 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: State of Libya
conventional short form: Libya
local long form: Dawiat Libiya
local short form: Libiya
etymology: name derives from the Libu, an ancient Libyan tribe first mentioned in texts from the 13th century B.C.
Government type
in transition
Capital
name: Tripoli (Tarabulus)
geographic coordinates: 32 53 N, 13 10 E
time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: originally founded by the Phoenicians as Oea in the 7th century B.C., the city changed rulers many times over the successive centuries; by the beginning of the 3rd century A.D. the region around the city was referred to as Regio Tripolitana by the Romans, meaning "region of the three cities" - namely Oea (i.e., modern Tripoli), Sabratha (to the west), and Leptis Magna (to the east); over time, the shortened name of "Tripoli" came to refer to just Oea, which derives from the Greek words "tria" and "polis" meaning "three cities"
Administrative divisions
22 governorates (muhafazah, singular - muhafazat); Al Butnan, Al Jabal al Akhdar, Al Jabal al Gharbi, Al Jafarah, Al Jufrah, Al Kufrah, Al Marj, Al Marqab, Al Wahat, An Nuqat al Khams, Az Zawiyah, Banghazi (Benghazi), Darnah, Ghat, Misratah, Murzuq, Nalut, Sabha, Surt, Tarabulus (Tripoli), Wadi al Hayat, Wadi ash Shati
Independence
24 December 1951 (from UN trusteeship)
National holiday
Liberation Day, 23 October (2011)
Constitution
history: previous 1951, 1977; in July 2017, the Constitutional Assembly completed and approved a draft of a new permanent constitution; in September 2018, the House of Representatives passed a constitutional referendum law in a session with contested reports of the quorum needed to pass the vote, and submitted it to the High National Elections Commission in December to begin preparations for a constitutional referendum
Legal system
Libya's post-revolution legal system is in flux and driven by state and non-state entities
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICC
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent or grandparent must be a citizen of Libya
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: varies from 3 to 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age, universal
Executive branch
chief of state: Chairman, Presidential Council, Mohammed Al MENFI (since 5 February 2021)
head of government: Prime Minister Abdul Hamid DBEIBEH (since 5 February 2021)
cabinet: GNA Presidency Council (pending approval by the House of Representatives - as of December 2018)
elections/appointments:
election originally scheduled for 24 December 2021, but will likely be postponed by the election commission until a list of candidates is resolved
election results: on 5 February 2021, a UN-led forum elected - in a runoff - Mohammed Al MENFI chairman, Presidential Council and Abdul Hamid DBEIBEH, prime minister
Legislative branch
description: unicameral House of Representatives (Majlis Al Nuwab) or HoR (200 seats including 32 reserved for women; 188 seats filled as of December 2021; members directly elected by majority vote; member term NA); note - the HoR elected on 25 June 2014 was dissolved on 4 August 2014 and since then has served as a temporary body until a permanent legislature is elected
elections: last held on 25 June 2014 ( next to be held on 24 January 2022)
election results: for election held on 25 June 2014 - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; composition - men 158, women 30, percent of women 16%; note - only 188 of the 200 seats were filled in the June 2014 election because of boycotts and lack of security at some polling stations; some elected members of the HoR also boycotted the election
Judicial branch
highest courts: NA; note - government is in transition
International organization participation
ABEDA, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AMU, AU, BDEAC, CAEU, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission:
Ambassador Wafa M.T. BUGHAIGHIS (since 29 November 2017)
chancery:
1460 Dahlia Street NW, Washington, DC 20012
telephone: [1] (202) 944-9601
FAX: [1] (202) 944-9606
email address and website:
info@embassyoflibyadc.com
https://www.embassyoflibyadc.org/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Richard B. NORLAND (since 22 August 2019)
embassy: Sidi Slim Area/Walie Al-Ahed Road, Tripoli (temporarily closed)
mailing address: 8850 Tripoli Place, Washington, DC 20521-8850
telephone: [216] 71-107-000
email address and website:
LibyaACS@state.gov
https://ly.usembassy.gov/
note: the US Embassy in Tripoli closed in July 2014 due to fighting near the embassy related to Libyan civil unrest; embassy staff and operations temporarily first relocated to Valetta, Malta and currently are temporarily relocated to Tunis, Tunisia
Flag description
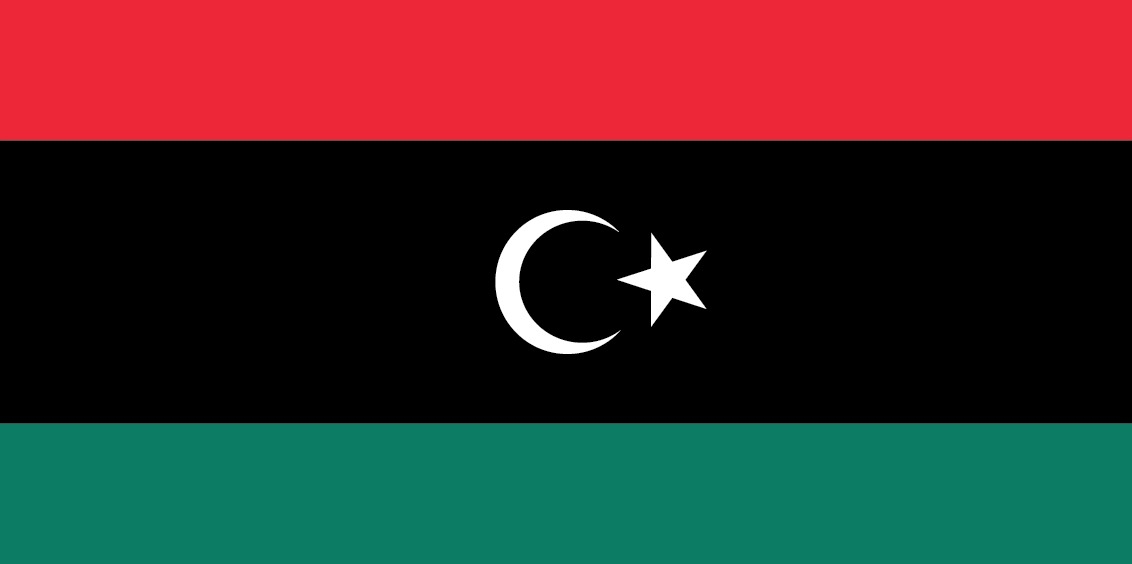
three horizontal bands of red (top), black (double width), and green with a white crescent and star centered on the black stripe; the National Transitional Council reintroduced this flag design of the former Kingdom of Libya (1951-1969) on 27 February 2011; it replaced the former all-green banner promulgated by the QADHAFI regime in 1977; the colors represent the three major regions of the country: red stands for Fezzan, black symbolizes Cyrenaica, and green denotes Tripolitania; the crescent and star represent Islam, the main religion of the country
National symbol(s)
star and crescent, hawk; national colors: red, black, green
National anthem
name: Libya, Libya, Libya
lyrics/music: Al Bashir AL AREBI/Mohamad Abdel WAHAB
note: also known as "Ya Beladi" or "Oh, My Country!"; adopted 1951; readopted 2011 with some modification to the lyrics; during the QADHAFI years between 1969 and 2011, the anthem was "Allahu Akbar," (God is Great) a marching song of the Egyptian Army in the 1956 Suez War
Economy
Economic overview
Libya's economy, almost entirely dependent on oil and gas exports, has struggled since 2014 given security and political instability, disruptions in oil production, and decline in global oil prices. The Libyan dinar has lost much of its value since 2014 and the resulting gap between official and black market exchange rates has spurred the growth of a shadow economy and contributed to inflation. The country suffers from widespread power outages, caused by shortages of fuel for power generation. Living conditions, including access to clean drinking water, medical services, and safe housing have all declined since 2011. Oil production in 2017 reached a five-year high, driving GDP growth, with daily average production rising to 879,000 barrels per day. However, oil production levels remain below the average pre-Revolution highs of 1.6 million barrels per day.
The Central Bank of Libya continued to pay government salaries to a majority of the Libyan workforce and to fund subsidies for fuel and food, resulting in an estimated budget deficit of about 17% of GDP in 2017. Low consumer confidence in the banking sector and the economy as a whole has driven a severe liquidity shortage.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$70.65 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$102.84 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$100.3 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
64% (2017 est.)
-7.4% (2016 est.)
-13% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$10,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$15,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$15,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$52.259 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
28.5% (2017 est.)
25.9% (2016 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 1.3% (2017 est.)
industry: 52.3% (2017 est.)
services: 46.4% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 71.6% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 19.4% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 2.7% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.3% (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 38.8% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -33.8% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
potatoes, watermelons, tomatoes, onions, dates, milk, olives, wheat, poultry, vegetables
Industries
petroleum, petrochemicals, aluminum, iron and steel, food processing, textiles, handicrafts, cement
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 17%
industry: 23%
services: 59% (2004 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: about one-third of Libyans live at or below the national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 15.78 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 23.46 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$2.574 billion (2017 est.)
-$4.575 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$29.96 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$11.99 billion (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
Italy 18%, China 16%, Germany 15%, Spain 15%, United Arab Emirates 6%, France 6%, United States 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, natural gas, gold, refined petroleum, scrap iron (2019)
Imports
$18.85 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$8.667 billion (2016 est.)
Imports - partners
China 16%, Turkey 14%, Italy 9%, United Arab Emirates 9%, Egypt 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, broadcasting equipment, cigarettes, jewelry (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$74.71 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$66.05 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$3.02 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$3.116 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Libyan dinars (LYD) per US dollar -
1.413 (2017 est.)
1.3904 (2016 est.)
1.3904 (2015 est.)
1.379 (2014 est.)
1.2724 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 48.7%
male: 40.8%
female: 67.8% (2012 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2019)
Electricity - production
34.24 billion kWh (2016 est.)
note: persistent electricity shortages have contributed to the ongoing instability throughout the country
Electricity - installed generating capacity
9.46 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from fossil fuels
100% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183Electricity - from other renewable sources
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198Crude oil - exports
337,800 bbl/day (2015 est.)
note: Libyan crude oil export values are highly volatile because of continuing protests and other disruptions across the country
Crude oil - proved reserves
48.36 billion bbl (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9Refined petroleum products - production
89,620 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69Refined petroleum products - consumption
260,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49Natural gas - proved reserves
1.505 trillion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1.576 million (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 23.95 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 6.02 million (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 91.48 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: political and security instability in Libya has disrupted its telecom sector, as warring factions make mobile towers a target and construction workers regularly cut cables by mistake; much of its infrastructure remains superior to that in most other African countries; rival operators fight for control; investment in fiber backbone and upgrades to international cables; limited LTE and 5G service; some satellite broadband; Chinese companies have heavily invested in Libyan infrastructure and now dominate the telecommunications sector; in 2021 Libya signed deals and projects with US firms to upgrade portions of its infrastructure, increasing the diversity of its telecommunications networks (2021)
domestic: 24 per 100 fixed-line and 91 per 100 mobile-cellular subscriptions; service generally adequate (2019)
international: country code - 218; landing points for LFON, EIG, Italy-Libya, Silphium and Tobrok-Emasaed submarine cable system connecting Europe, Africa, the Middle East and Asia; satellite earth stations - 4 Intelsat, Arabsat, and Intersputnik; microwave radio relay to Tunisia and Egypt; tropospheric scatter to Greece; participant in Medarabtel (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
state-funded and private TV stations; some provinces operate local TV stations; pan-Arab satellite TV stations are available; state-funded radio (2019)
Internet users
total: 3.19 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 21.76% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 318,000 (2017 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4.83 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 9 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 55
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 927,153 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 68
over 3,047 m: 23
2,438 to 3,047 m: 7
1,524 to 2,437 m: 30
914 to 1,523 m: 7
under 914 m: 1 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 78
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 14
914 to 1,523 m: 37
under 914 m: 20 (2013)
Heliports
2 (2013)
Pipelines
882 km condensate, 3743 km gas, 7005 km oil (2013)
Roadways
total: 37,000 km (2010)
paved: 34,000 km (2010)
unpaved: 3,000 km (2010)
Merchant marine
total: 94
by type: general cargo 2, oil tanker 12, other 80 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Marsa al Burayqah (Marsa el Brega), Tripoli
oil terminal(s): Az Zawiyah, Ra's Lanuf
LNG terminal(s) (export): Marsa el Brega
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Libya lacks a nationwide military and the interim government, the Government of National Unity (GNU), relies on its cooperation with disparate militias that it cannot entirely control for security; the GNU has access to various ground, air, and naval/coast guard forces comprised of a mix of semi-regular military units, militias, civilian volunteers, and foreign troops and mercenaries
the Libyan National Army (LNA), under de facto LNA commander Khalifa HAFTER, also includes various ground, air, and naval units comprised of semi-regular military personnel, militias, and foreign troops and mercenaries; as of late 2021, the LNA continued to operate independently from the GNU and exerted influence throughout eastern, central, and southern Libya (2021)
Military expenditures
not available
Military and security service personnel strengths
estimates not available
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
both the forces aligned with the GNU and the LNA are largely equipped with weapons of Russian or Soviet origin; as of 2021, Turkey was providing arms and equipment to the forces supporting the GNU, while Russia was the main supporter of the LNA (2021)
Military - note
in April 2019, Libyan National Army (LNA) forces launched an offensive to seize the capital, Tripoli, from the UN-recognized GNU (aka Government of National Accord or GNA); the GNU and its local supporting militia forces forced the LNA to withdraw by June 2020; at the signing of a UN-sponsored ceasefire in October 2020, GNU and LNA forces were separated by a line of control running roughly from the coastal city of Sirte south to the vicinity of Al Jufra and Brak; as of late 2021, this line had grown increasingly fortified; in April 2021, the UN Security Council endorsed plans to deploy civilian ceasefire monitoring personnel at the request of the Libyans
outside actors have played a large role in the fighting in Libya on both sides:
as of 2021, GNU forces were backed militarily by Qatar and Turkey; Turkey has been the chief supporter; it signed a security agreement with the GNU in 2019, and Turkey’s aid was assessed as vital in turning back the LNA offensive in 2019-2020; Turkey’s support has included air defense, unmanned aerial vehicles (aka drones), equipment, weapons, training, and military personnel, including advisors, technicians, and equipment operators; in addition, Turkey has provided as many as 5,000 mercenary fighters from Syria
as of 2021, LNA forces (aka Libyan Arab Armed Forces, LAAF) have received varying amounts of military support from Chad, Egypt, France, Jordan, Russia, Sudan, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE); Russia, Sudan, and the UAE have been the most active; Russia has provided equipment, weapons, aircraft, and air defense support, as well as an estimated 5,000 Russian mercenaries/private military contractors and Russian-sponsored Syrian mercenary fighters; Sudan reportedly provided at least 1,000 troops from its Rapid Support Forces in 2019-2020 and more than 1,000 Sudanese mercenaries were present in Libya as of late 2021; the UAE provided equipment, supplies, weapons, and air support, including air strikes from manned and unmanned aircraft; meanwhile, Egypt has provided arms, supplies, and training, as well as facilitated both Emirati and Russian operations in Libya by allowing them to use the country’s western bases and to transport arms over the border
as of late 2021, it was estimated that as many as 20,000 third-country nationals were involved in military operations in Libya, despite the confidence building measure of the October 2020 ceasefire that called for all foreign forces to leave the country by early 2021; in addition to the military and proxy forces provided by Russia, Sudan, and Turkey, foreign fighters from Libya’s neighbors (Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Mali, Niger, and Tunisia, as well as Sudan) have travelled to Libya since the civil war began in 2011 to support various armed groups, including those aligned with the GNU and the LNA, as well as the Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham and Al Qa’ida terrorist group affiliates operating in Libya; most of these fighters arrived as individuals, but rebel groups from Chad and Sudan were also reportedly involved in the fighting
Military service age and obligation
not available
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Ansar al-Sharia groups; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham – Libya; al-Mulathamun Battalion (al-Mourabitoun); al-Qa'ida in the Islamic Maghreb
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
dormant disputes include Libyan claims of about 32,000 sq km still reflected on its maps of southeastern Algeria and the FLN's assertions of a claim to Chirac Pastures in southeastern Morocco; various Chadian rebels from the Aozou region reside in southern Libya
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 17,733 (Sudan) (refugees and asylum seekers), 14,194 (Syria) (refugees and asylum seekers) (2021)
IDPs: 199,949 (conflict between pro-QADHAFI and anti-QADHAFI forces in 2011; post-QADHAFI tribal clashes 2014) (2021)