Senegal
Introduction
Background
Senegal is one of the few countries in the world with evidence of continuous human life from the Paleolithic era to present. Between the 14th and 16th centuries, the Jolof Empire ruled most of Senegal. Starting in the 15th century, Portugal, the Netherlands, France, and Great Britain traded along the Senegalese coast. Senegal’s location on the western tip of Africa made it a favorable base for the European slave trade. European powers used the Senegalese island of Goree as a base to purchase slaves from the warring chiefdoms on the mainland, and at the height of the slave trade in Senegal, over one-third of the Senegalese population was enslaved. In 1815, France abolished slavery and began expanding inland. During the second half of the 19th century, France took possession of Senegal as a French colony. In 1959, the French colonies of Senegal and French Sudan were merged and granted independence in 1960 as the Mali Federation. The union broke up after only a few months. In 1982, Senegal joined with The Gambia to form the nominal confederation of Senegambia. The envisaged integration of the two countries was never implemented, and the union dissolved in 1989.
Since the 1980s, the Movement of Democratic Forces in the Casamance - a separatist movement based in southern Senegal - has led a low-level insurgency. Several attempts at reaching a comprehensive peace agreement have failed. Since 2012, despite sporadic incidents of violence, an unofficial cease-fire has remained largely in effect. Senegal is one of the most stable democracies in Africa and has a long history of participating in international peacekeeping and regional mediation. The Socialist Party of Senegal ruled for 40 years until Abdoulaye WADE was elected president in 2000 and re-elected in 2007. WADE amended Senegal's constitution over a dozen times to increase executive power and weaken the opposition. In 2012, WADE’s decision to run for a third presidential term sparked public backlash that led to his defeat to current President Macky SALL. A 2016 constitutional referendum limited future presidents to two consecutive five-year terms. The change, however, does not apply to SALL's first term. In February 2019, SALL won his bid for re-election; his second term will end in 2024. One month after the 2019 election, the National Assembly voted to abolish the office of the prime minister. Opposition and civil society organizations criticized the decision as a further concentration of power in the executive branch at the expense of the legislative and judicial branches.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
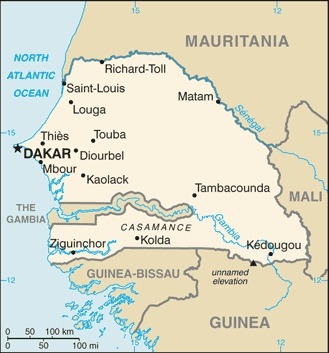
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea-Bissau and Mauritania
Geographic coordinates
14 00 N, 14 00 W
Map references
Africa
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than South Dakota; slightly larger than twice the size of Indiana
Land boundaries
total: 2,684 km
border countries (5): The Gambia 749 km, Guinea 363 km, Guinea-Bissau 341 km, Mali 489 km, Mauritania 742 km
Coastline
531 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
Climate
tropical; hot, humid; rainy season (May to November) has strong southeast winds; dry season (December to April) dominated by hot, dry, harmattan wind
Terrain
generally low, rolling, plains rising to foothills in southeast
Elevation
highest point: unnamed elevation 2.8 km southeast of Nepen Diaka 648 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 69 m
Natural resources
fish, phosphates, iron ore
Land use
agricultural land: 46.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 17.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 29.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.8% (2018 est.)
other: 9.4% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
1,200 sq km (2012)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Senegal (shared with Guinea [s], Mali, and Mauritania [m] ) - 1,641 km; Gambia (shared with Guinea [s] and The Gambia [m]) - 1,094 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Senegal (456,397 sq km)
Major aquifers
Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin
Population distribution
the population is concentrated in the west, with Dakar anchoring a well-defined core area; approximately 70% of the population is rural as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
lowlands seasonally flooded; periodic droughts
Geography - note
westernmost country on the African continent; The Gambia is almost an enclave within Senegal
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Senegalese (singular and plural)
adjective: Senegalese
Ethnic groups
Wolof 37.1%, Pular 26.2%, Serer 17%, Mandinka 5.6%, Jola 4.5%, Soninke 1.4%, other 8.3% (includes Europeans and persons of Lebanese descent) (2017 est.)
Languages
French (official), Wolof, Pular, Jola, Mandinka, Serer, Soninke
Religions
Muslim 95.9% (most adhere to one of the four main Sufi brotherhoods), Christian 4.1% (mostly Roman Catholic) (2017 est.)
Demographic profile
Senegal has a large and growing youth population but has not been successful in developing its potential human capital. Senegal’s high total fertility rate of almost 4.5 children per woman continues to bolster the country’s large youth cohort – more than 60% of the population is under the age of 25. Fertility remains high because of the continued desire for large families, the low use of family planning, and early childbearing. Because of the country’s high illiteracy rate (more than 40%), high unemployment (even among university graduates), and widespread poverty, Senegalese youths face dim prospects; women are especially disadvantaged.
Senegal historically was a destination country for economic migrants, but in recent years West African migrants more often use Senegal as a transit point to North Africa – and sometimes illegally onward to Europe. The country also has been host to several thousand black Mauritanian refugees since they were expelled from their homeland during its 1989 border conflict with Senegal. The country’s economic crisis in the 1970s stimulated emigration; departures accelerated in the 1990s. Destinations shifted from neighboring countries, which were experiencing economic decline, civil wars, and increasing xenophobia, to Libya and Mauritania because of their booming oil industries and to developed countries (most notably former colonial ruler France, as well as Italy and Spain). The latter became attractive in the 1990s because of job opportunities and their periodic regularization programs (legalizing the status of illegal migrants).
Additionally, about 16,000 Senegalese refugees still remain in The Gambia and Guinea-Bissau as a result of more than 30 years of fighting between government forces and rebel separatists in southern Senegal’s Casamance region.
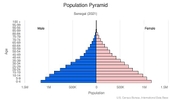
Age structure
0-14 years: 40.38% (male 3,194,454/female 3,160,111)
15-24 years: 20.35% (male 1,596,896/female 1,606,084)
25-54 years: 31.95% (male 2,327,424/female 2,700,698)
55-64 years: 4.21% (male 283,480/female 378,932)
65 years and over: 3.1% (male 212,332/female 275,957) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 84.2
youth dependency ratio: 78.4
elderly dependency ratio: 5.7
potential support ratio: 17.5 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 19.4 years
male: 18.5 years
female: 20.3 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the population is concentrated in the west, with Dakar anchoring a well-defined core area; approximately 70% of the population is rural as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 48.6% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.59% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.230 million DAKAR (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.86 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.75 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
21.9 years (2018 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
315 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35Infant mortality rate
total: 47.72 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 54.66 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 40.58 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 63.83 years
male: 61.59 years
female: 66.14 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
26.9% (2019)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 92.3% of population
rural: 74.5% of population
total: 83.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 6.7% of population
rural: 25.5% of population
total: 16.7% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
4% (2018)
Physicians density
0.07 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 91.2% of population
rural: 48.5% of population
total: 68.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 8.8% of population
rural: 51.5% of population
total: 31.6% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 51.9%
male: 64.8%
female: 39.8% (2017)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years
male: 8 years
female: 9 years (2020)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 4.1%
male: 2.9%
female: 6.7% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; periodic droughts; seasonal flooding; overfishing; weak environmental protective laws; wildlife populations threatened by poaching
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 37.52 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 10.9 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 11.74 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; hot, humid; rainy season (May to November) has strong southeast winds; dry season (December to April) dominated by hot, dry, harmattan wind
Land use
agricultural land: 46.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 17.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 29.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.8% (2018 est.)
other: 9.4% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 48.6% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.59% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 1.46% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Food insecurity
severe localized food insecurity: due to localized shortfalls in cereal production - according to the latest analysis, about 490,000 people are estimated to need humanitarian assistance in the June−August 2021 period due to the effects of adverse weather events (droughts and floods) on cereal and fodder production (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2,454,059 tons (2016 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Senegal (shared with Guinea [s], Mali, and Mauritania [m] ) - 1,641 km; Gambia (shared with Guinea [s] and The Gambia [m]) - 1,094 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Senegal (456,397 sq km)
Major aquifers
Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 98 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 58 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 2.065 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
38.97 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Senegal
conventional short form: Senegal
local long form: Republique du Senegal
local short form: Senegal
former: Senegambia (along with The Gambia), Mali Federation
etymology: named for the Senegal River that forms the northern border of the country; many theories exist for the origin of the river name; perhaps the most widely cited derives the name from "Azenegue," the Portuguese appellation for the Berber Zenaga people who lived north of the river
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Dakar
geographic coordinates: 14 44 N, 17 38 W
time difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the Atlantic coast trading settlement of Ndakaaru came to be called "Dakar" by French colonialists
Administrative divisions
14 regions (regions, singular - region); Dakar, Diourbel, Fatick, Kaffrine, Kaolack, Kedougou, Kolda, Louga, Matam, Saint-Louis, Sedhiou, Tambacounda, Thies, Ziguinchor
Independence
4 April 1960 (from France); note - complete independence achieved upon dissolution of federation with Mali on 20 August 1960
National holiday
Independence Day, 4 April (1960)
Constitution
history: previous 1959 (preindependence), 1963; latest adopted by referendum 7 January 2001, promulgated 22 January 2001
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or by the National Assembly; passage requires Assembly approval and approval in a referendum; the president can bypass a referendum and submit an amendment directly to the Assembly, which requires at least three-fifths majority vote; the republican form of government is not amendable; amended several times, last in 2019
Legal system
civil law system based on French law; judicial review of legislative acts in Constitutional Court
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Senegal
dual citizenship recognized: no, but Senegalese citizens do not automatically lose their citizenship if they acquire citizenship in another state
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Macky SALL (since 2 April 2012)
head of government: On 11 December 2021, the National Assembly approved a constitutional amendment re-establishing the position of Prime Minister which SALL eliminated after his re-election in 2019. The new Prime Minister will be appointed in early 2022.
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a single renewable 5-year term; election last held on 24 February 2019 (next to be held in February 2024)
election results: Macky SALL elected president in first round; percent of vote - Macky SALL (APR) 58.3%, Idrissa SECK (Rewmi) 20.5%, Ousmane SONKO (PASTEF) 15.7%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Assembly or Assemblée Nationale (165 seats; 105 members including 15 representing Senegalese diaspora directly elected by plurality vote in single- and multi-seat constituencies and 60 members directly elected by proportional representation vote in single- and multi-seat constituencies)
elections: National Assembly - last held on 2 July 2017 (next to be held in July 2022)
election results: National Assembly results - percent of vote by party/coalition - BBK 49.5%, CGWS 16.7%, MTS 11.7%, PUR 4.7%, CP-Kaddu Askan Wi 2%, other 15.4%; seats by party/coalition - BBY 125, CGWS 19, MTS 7, PUR 3, CP-Kaddu Askan Wi 2, other 9; composition - men 96, women 69, percent of women 41.8%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (consists of the court president and 12 judges and organized into civil and commercial, criminal, administrative, and social chambers); Constitutional Council or Conseil Constitutionel (consists of 7 members, including the court president, vice president, and 5 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president of the republic upon recommendation of the Superior Council of the Magistrates, a body chaired by the president and minister of justice; judge tenure varies, with mandatory retirement either at 65 or 68 years; Constitutional Council members appointed - 5 by the president and 2 by the National Assembly speaker; judges serve 6-year terms, with renewal of 2 members every 2 years
subordinate courts: High Court of Justice (for crimes of high treason by the president); Courts of Appeal; Court of Auditors; assize courts; regional and district courts; Labor Court
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for the Republic-Yakaar or APR-Yakaar [Macky SALL]
Alliance of Forces of Progress or AFP [Moustapha NIASSE]
Alliance for Citizenship and Labor or ACT [Abdoul MBAYE]
And-Jef/African Party for Democracy and Socialism or AJ/PADS [Mamadou DIOP Decriox]
Benno Bokk Yakaar or BBY (United in Hope) [Macky SALL] (coalition includes AFP, APR, BGC, LD-MPT, PIT, PS, and UNP)
Bokk Gis Gis coalition [Pape DIOP]
Citizen Movement for National Reform or MCRN-Bes Du Nakk [Mansour Sy DJAMIL]
Democratic League-Labor Party Movement or LD-MPT [Abdoulaye BATHILY]
Dare the Future movement [Aissata Tall SALL]
Front for Socialism and Democracy/Benno Jubel or FSD/BJ [Cheikh Abdoulaye Bamba DIEYE]
Gainde Centrist Bloc or BGC [Jean-Paul DIAS]
General Alliance for the Interests of the Republic or AGIR [Thierno BOCOUM]
Grand Party or GP [Malick GAKOU]
Independence and Labor Party or PIT [Magatte THIAM]
Madicke 2019 coalition [Madicke NIANG]
National Union for the People or UNP [Souleymane Ndene NDIAYE]
Only Senegal movement [Pierre Goudiaby ATEPA]
Party for Truth and Development or PVD [Cheikh Ahmadou Kara MBAKE]
Party of Unity and Rally or PUR [El Hadji SALL]
Patriotic Convergence Kaddu Askan Wi or CP-Kaddu Askan Wi [Abdoulaye BALDE]
Patriots of Senegal for Ethics, Work and Fraternity or (PASTEF) [Ousmane SONKO]
Rewmi Party [Idrissa SECK]
Senegalese Democratic Party or PDS [Abdoulaye WADE]
Socialist Party or PS [Ousmane Tanor DIENG]
Tekki Movement [Mamadou Lamine DIALLO]
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, CPLP (associate), ECOWAS, EITI (candidate country), FAO, FZ, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Mansour Elimane KANE (since 6 January 2020)
chancery: 2215 M Street NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 234-0540
FAX: [1] (202) 629-2961
email address and website:
contact@ambasenegal-us.org
http://www.ambasenegal-us.org/index.php
consulate(s) general: Houston, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Tulinabo S. MUSHINGI (since August 2017); note - also accredited to Guinea-Bissau
embassy: Route des Almadies, Dakar
mailing address: 2130 Dakar Place, Washington DC 20521-2130
telephone: [221] 33-879-4000
email address and website:
DakarACS@state.gov
https://sn.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), yellow, and red with a small green five-pointed star centered in the yellow band; green represents Islam, progress, and hope; yellow signifies natural wealth and progress; red symbolizes sacrifice and determination; the star denotes unity and hope
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; the colors from left to right are the same as those of neighboring Mali and the reverse of those on the flag of neighboring Guinea
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: green, yellow, red
National anthem
name: "Pincez Tous vos Koras, Frappez les Balafons" (Pluck Your Koras, Strike the Balafons)
lyrics/music: Leopold Sedar SENGHOR/Herbert PEPPER
note: adopted 1960; lyrics written by Leopold Sedar SENGHOR, Senegal's first president; the anthem sometimes played incorporating the Koras (harp-like stringed instruments) and Balafons (types of xylophones) mentioned in the title
Economy
Economic overview
Senegal’s economy is driven by mining, construction, tourism, fisheries and agriculture, which are the primary sources of employment in rural areas. The country's key export industries include phosphate mining, fertilizer production, agricultural products and commercial fishing and Senegal is also working on oil exploration projects. It relies heavily on donor assistance, remittances and foreign direct investment. Senegal reached a growth rate of 7% in 2017, due in part to strong performance in agriculture despite erratic rainfall.
President Macky SALL, who was elected in March 2012 under a reformist policy agenda, inherited an economy with high energy costs, a challenging business environment, and a culture of overspending. President SALL unveiled an ambitious economic plan, the Emerging Senegal Plan (ESP), which aims to implement priority economic reforms and investment projects to increase economic growth while preserving macroeconomic stability and debt sustainability. Bureaucratic bottlenecks and a challenging business climate are among the perennial challenges that may slow the implementation of this plan.
Senegal receives technical support from the IMF under a Policy Support Instrument (PSI) to assist with implementation of the ESP. The PSI implementation continues to be satisfactory as concluded by the IMF’s fifth review in December 2017. Financial markets have signaled confidence in Senegal through successful Eurobond issuances in 2014, 2017, and 2018.
The government is focusing on 19 projects under the ESP to continue The government’s goal under the ESP is structural transformation of the economy. Key projects include the Thiès-Touba Highway, the new international airport opened in December 2017, and upgrades to energy infrastructure. The cost of electricity is a chief constraint for Senegal’s development. Electricity prices in Senegal are among the highest in the world. Power Africa, a US presidential initiative led by USAID, supports Senegal’s plans to improve reliability and increase generating capacity.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$55.26 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$54.78 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$52.47 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
7.2% (2017 est.)
6.2% (2016 est.)
6.4% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$3,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$3,400 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$3,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$23.576 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
-0.8% (2019 est.)
0.4% (2018 est.)
1.3% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: Ba3 (2017)
Standard & Poors rating: B+ (2000)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 16.9% (2017 est.)
industry: 24.3% (2017 est.)
services: 58.8% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 71.9% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 15.2% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 25.1% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 3.4% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 27% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -42.8% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
groundnuts, watermelons, rice, sugar cane, cassava, millet, maize, onions, sorghum, vegetables
Industries
agricultural and fish processing, phosphate mining, fertilizer production, petroleum refining, zircon, and gold mining, construction materials, ship construction and repair
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 77.5%
industry: 22.5%
industry and services: 22.5% (2007 est.)
Population below poverty line
46.7% (2011 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
40.3 (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.5%
highest 10%: 31.1% (2011)
Budget
revenues: 4.139 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 4.9 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$1.547 billion (2017 est.)
-$769 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$5.29 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$2.498 billion (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
Mali 22%, Switzerland 14%, India 9%, China 7% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, refined petroleum, phosphoric acid, fish, ground nuts (2019)
Imports
$8.96 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$4.966 billion (2016 est.)
Imports - partners
China 17%, France 11%, Belgium 7%, Russia 7%, Netherlands 7% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, crude petroleum, rice, cars, malt extract, clothing and apparel (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$1.827 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$116.9 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$8.571 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$6.327 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar -
617.4 (2017 est.)
593.01 (2016 est.)
593.01 (2015 est.)
591.45 (2014 est.)
494.42 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 4.1%
male: 2.9%
female: 6.7% (2019 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 71% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 94% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 50% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
977,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129Electricity - from fossil fuels
82% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
7% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127Electricity - from other renewable sources
11% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79Refined petroleum products - production
17,590 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90Refined petroleum products - consumption
48,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 207,592 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.27 (2019 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 19,078,948 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 114 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: universal mobile penetration since 2019; mobile broadband accounts for 97% of Internet access; 3G and LTE services for half of the population; African consortium issued a bond to finance network upgrades and services; importer of broadcasting equipment from UAE and China (2020)
domestic: generally reliable urban system with a fiber-optic network; about two-thirds of all fixed-line connections are in Dakar; mobile-cellular service is steadily displacing fixed-line service, even in urban areas; fixed-line 1 per 100 and mobile-cellular 110 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 221; landing points for the ACE, Atlantis-2, MainOne and SAT-3/WASC submarine cables providing connectivity from South Africa, numerous western African countries, Europe and South America; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
state-run Radiodiffusion Television Senegalaise (RTS) broadcasts TV programs from five cities in Senegal; in most regions of the country, viewers can receive TV programming from at least 7 private broadcasters; a wide range of independent TV programming is available via satellite; RTS operates a national radio network and a number of regional FM stations; at least 7 community radio stations and 18 private-broadcast radio stations are available; transmissions of at least 5 international broadcasters are accessible on FM in Dakar (2019)
Internet users
total: 7.81 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 46% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 177,363 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.06 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 11
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 21,038 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 40,000 mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 9
over 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 6
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 11
1,524 to 2,437 m: 7
914 to 1,523 m: 3
under 914 m: 1 (2013)
Pipelines
43 km gas, 8 km refined products (2017)
Railways
total: 906 km (713 km operational in 2017) (2017)
narrow gauge: 906 km 1.000-m gauge (2017)
Roadways
total: 16,665 km (2017)
paved: 6,126 km (includes 241 km of expressways) (2017)
unpaved: 10,539 km (2017)
Waterways
1,000 km (primarily on the Senegal, Saloum, and Casamance Rivers) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 63Merchant marine
total: 35
by type: general cargo 5, oil tanker 1, other 29 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Dakar
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Senegalese Armed Forces (Forces Armées Sénégalaises, FAS): Army, Senegalese National Navy (Marine Senegalaise, MNS), Senegalese Air Force (Armee de l'Air du Senegal), National Gendarmerie (includes Territorial and Mobile components); Ministry of Interior: National Police (2021)
note - the National Police operates in major cities, while the Gendarmerie primarily operates outside urban areas
Military expenditures
1.5% of GDP (2020)
1.5% of GDP (2019 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2018)
1.5% of GDP (2017)
1.6% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Senegalese Armed Forces consist of approximately 19,000 active personnel (12,000 Army; 1,000 Navy/Coast Guard; 1,000 Air Force; 5,000 National Gendarmerie) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the FAS inventory includes mostly older or second-hand equipment from a variety of countries, including France, South Africa, and Russia/former Soviet Union; in recent years, the FAS has been undergoing a significant modernization program; since 2010, it has received newer equipment from nearly 15 countries, led by China, France, and Israel (2020)
Military deployments
750 Gambia (ECOMIG); 1,000 Mali (MINUSMA) (2021)
note - in 2021, Senegal also had over 700 police deployed on UN missions
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; 20 years of age for selective conscript service; 2-year service obligation; women have been accepted into military service since 2008 (2019)
Military - note
as of 2021, Senegalese security forces continued to be engaged in a low-level counterinsurgency campaign in the southern Casamance region against various factions of the separatist Movement of Democratic Forces of the Casamance; while violent incidents have decreased since a tacit cease-fire was reached in 2012, the insurgency, which began in 1982, remains one of longest running low-level conflicts in the world, claiming more than 5,000 lives and leaving another 60,000 displaced
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
cross-border trafficking in persons, timber, wildlife, and cannabis; rebels from the Movement of Democratic Forces in the Casamance find refuge in Guinea-Bissau
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 14,199 (Mauritania) (2021)
IDPs: 8,400 (2020)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: Senegal is a source, transit, and destination country for children and women who are subjected to forced begging, forced labor, and sex trafficking; traffickers subject Senegalese children to forced labor in domestic service, mining, and prostitution; some Senegalese boys from Quranic schools and boys from The Gambia, Mali, Guinea-Bissau, and Guinea are forced to beg; Senegalese women and girls are forced into domestic servitude in neighboring countries, Europe, and the Middle East, while others are sexually exploited in Senegal; women and girls from other West African countries are subjected to domestic servitude and sexual exploitation in Senegal; Ukrainian and Chinese women are exploited for sex trafficking in bars and nightclubs; North Korean workers are forced to work in construction
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Senegal does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; efforts include establishing an anti-trafficking database; planning the third phase of its program to remove vulnerable children, including trafficking victims, from the streets of major cities; launching an emergency campaign to place vulnerable children and forced begging victims in shelters due to COVID 19 pandemic; however, the government rarely proactively investigated or prosecuted traffickers exploiting children in forced begging; authorities did not take action against officials who refused to investigate such cases; officials only applied adequate prison terms in accordance with the 2005 anti-trafficking law to two convicted traffickers; authorities did not identify any adult trafficking victims; government officials continued to have a limited knowledge of trafficking; Senegal was downgraded to Tier 2 Watch List (2020)
Illicit drugs
major transit point on the cocaine route from South America to Europe; the third-largest cannabis-producing country in West Africa