Introduction
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
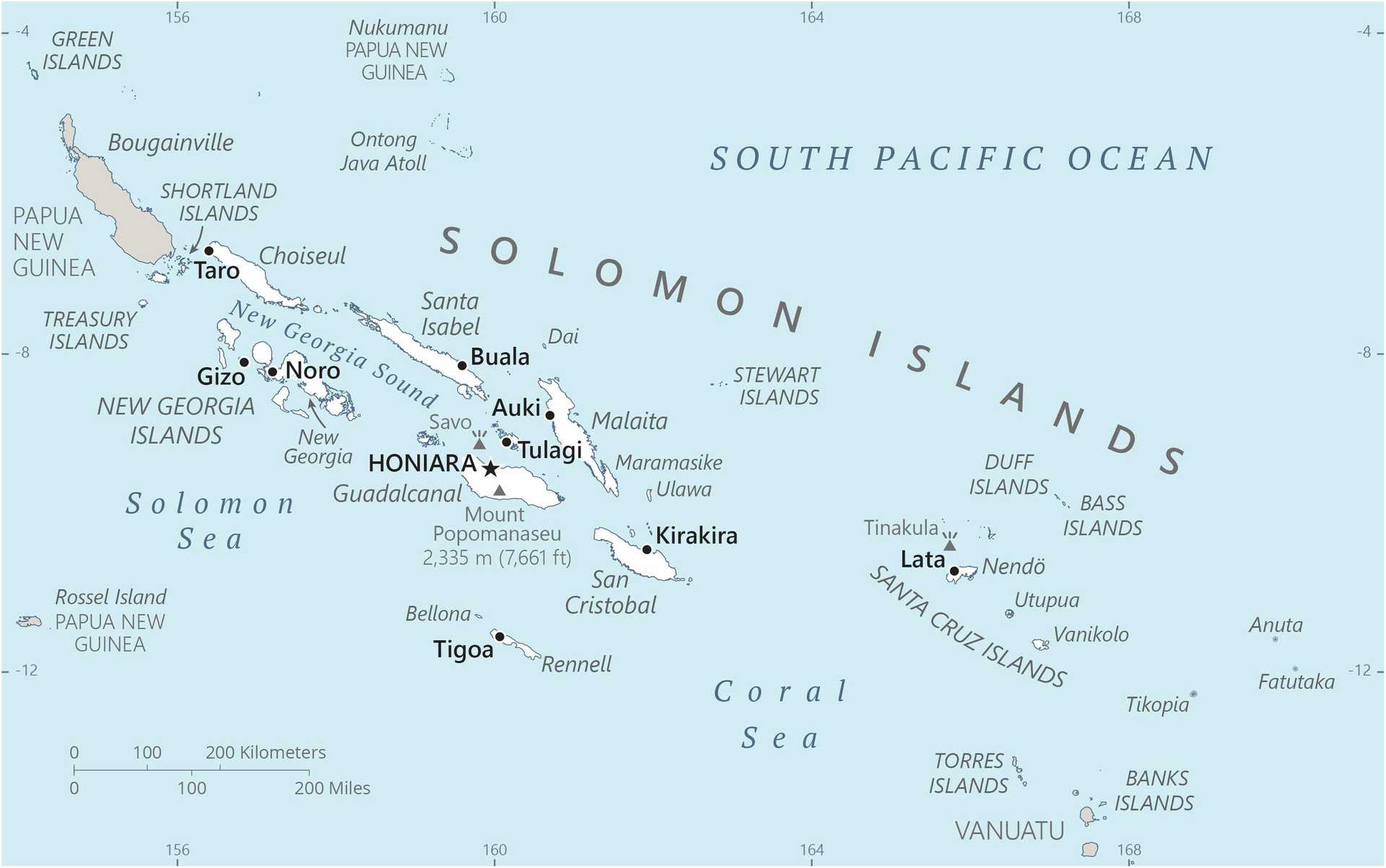
Geography
People and Society
Population
comparison rankings: total 167; male 167; female 167
Median age
comparison ranking: total 171
Population growth rate
comparison ranking: 57
Birth rate
comparison ranking: 54
Death rate
comparison ranking: 216
Net migration rate
comparison ranking: 157
Maternal mortality ratio
comparison ranking: 59
Infant mortality rate
comparison ranking: total 79
Life expectancy at birth
comparison ranking: total population 95
Total fertility rate
comparison ranking: 56
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
comparison ranking: 75
Alcohol consumption per capita
comparison ranking: total 146
Tobacco use
comparison ranking: total 6
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
comparison ranking: 30
Education expenditure
comparison ranking: Education expenditure (% GDP) 9
Environment
Carbon dioxide emissions
comparison ranking: total emissions 196
Government
Economy
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
comparison ranking: 197
Real GDP growth rate
comparison ranking: 136
Real GDP per capita
comparison ranking: 203
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
comparison ranking: 151
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
comparison rankings: agriculture 7; industry 140; services 161
Industrial production growth rate
comparison ranking: 50
Labor force
comparison ranking: 160
Unemployment rate
comparison ranking: 9
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
comparison ranking: total 181
Public debt
comparison ranking: 189
Taxes and other revenues
comparison ranking: 46
Current account balance
comparison ranking: 92
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
comparison ranking: 151
Debt - external
comparison ranking: 121
Energy
Electricity
comparison rankings: installed generating capacity 199; consumption 199; transmission/distribution losses 25
Energy consumption per capita
comparison ranking: 168
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 194
Telephones - mobile cellular
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 176
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
comparison ranking: total 209
Transportation
Merchant marine
comparison ranking: total 142