Introduction
Background
The lands that today comprise Croatia were part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire until the end of World War I. In 1918, the Croats, Serbs, and Slovenes formed a kingdom known after 1929 as Yugoslavia. Following World War II, Yugoslavia became a federal independent communist state consisting of six socialist republics, including Croatia, under the strong hand of Josip Broz, aka TITO. Although Croatia declared its independence from Yugoslavia in 1991, it took four years of sporadic, but often bitter, fighting before Yugoslav forces were cleared from Croatian lands, along with a majority of Croatia's ethnic Serb population. Under UN supervision, the last Serb-held enclave in eastern Slavonia was returned to Croatia in 1998. The country joined NATO in 2009 and the EU in 2013. In January 2023, Croatia further integrated into the EU by joining the Eurozone and the Schengen Area.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
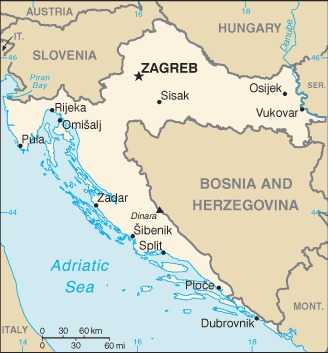
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea, between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Slovenia
Geographic coordinates
45 10 N, 15 30 E
Map references
Europe
Land boundaries
total: 2,237 km
border countries (5): Bosnia and Herzegovina 956 km; Hungary 348 km; Montenegro 19 km; Serbia 314 km; Slovenia 600 km
Coastline
5,835 km (mainland 1,777 km, islands 4,058 km)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate
Mediterranean and continental; continental climate predominant with hot summers and cold winters; mild winters, dry summers along coast
Terrain
geographically diverse; flat plains along Hungarian border, low mountains and highlands near Adriatic coastline and islands
Elevation
highest point: Dinara 1,831 m
lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 331 m
Natural resources
oil, some coal, bauxite, low-grade iron ore, calcium, gypsum, natural asphalt, silica, mica, clays, salt, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 23.7% (2018 est.)
arable land: 16% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 6.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 34.4% (2018 est.)
other: 41.9% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
171 sq km (2020)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Dunav (Danube) (shared with Germany [s], Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Serbia, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania [m]) - 2,888 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km)
Population distribution
more of the population lives in the northern half of the country, with approximately a quarter of the populace residing in and around the capital of Zagreb; many of the islands are sparsely populated
Natural hazards
destructive earthquakes
Geography - note
controls most land routes from Western Europe to Aegean Sea and Turkish Straits; most Adriatic Sea islands lie off the coast of Croatia -- some 1,200 islands, islets, ridges, and rocks
People and Society
Population
total: 4,150,116
male: 2,003,431
female: 2,146,685 (2024 est.)
comparison rankings: female 129; male 130; total 129
Nationality
noun: Croat(s), Croatian(s)
adjective: Croatian
note: the French designation of "Croate" to Croatian mercenaries in the 17th century eventually became "Cravate" and later came to be applied to the soldiers' scarves - the cravat; Croatia celebrates Cravat Day every 18 October
Ethnic groups
Croat 91.6%, Serb 3.2%, other 3.9% (including Bosniak, Romani, Albanian, Italian, and Hungarian), unspecified 1.3% (2021 est.)
Languages
Croatian (official) 95.2%, Serbian 1.2%, other 3.1% (including Bosnian, Romani, Albanian, and Italian) unspecified 0.5% (2021 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Knjiga svjetskih činjenica, nužan izvor osnovnih informacija. (Croatian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 79%, Orthodox 3.3%, Protestant 0.3%, other Christian 4.8%, Muslim 1.3%, other 1.1%, agnostic 1.7%, none or atheist 4.7%, unspecified 3.9% (2021 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 13.8% (male 296,527/female 278,236)
15-64 years: 63.1% (male 1,307,814/female 1,309,394)
65 years and over: 23.1% (2024 est.) (male 399,090/female 559,055)
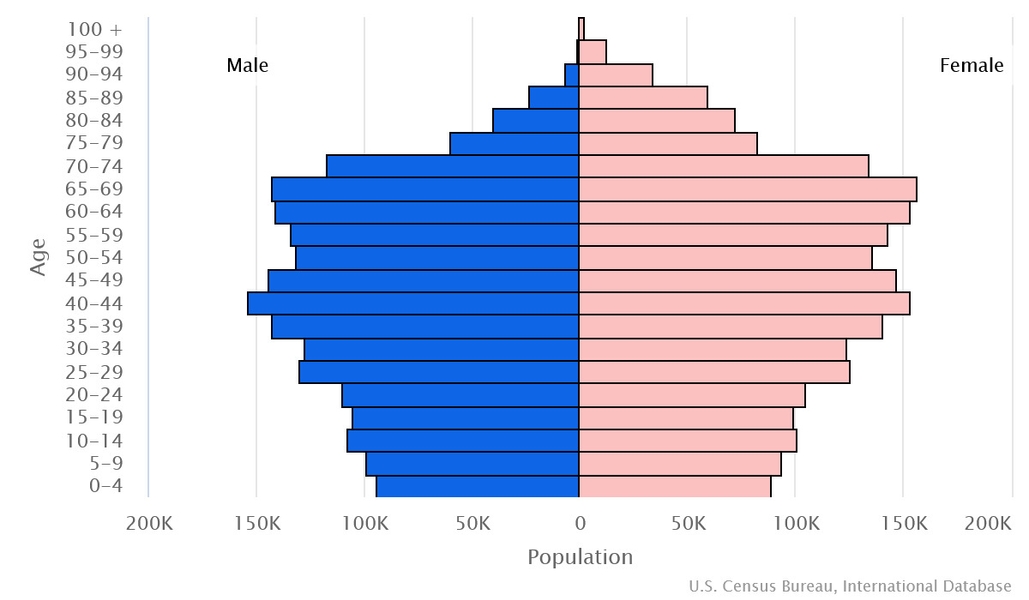
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 56.5
youth dependency ratio: 22.1
elderly dependency ratio: 34.4
potential support ratio: 2.9 (2021 est.)
Population distribution
more of the population lives in the northern half of the country, with approximately a quarter of the populace residing in and around the capital of Zagreb; many of the islands are sparsely populated
Urbanization
urban population: 58.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.05% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
684,000 ZAGREB (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female
total population: 0.93 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
29 years (2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 8.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2024 est.)
male: 8.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 8.7 deaths/1,000 live births
comparison ranking: total 143
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 77.7 years (2024 est.)
male: 74.6 years
female: 81 years
comparison ranking: total population 86
Gross reproduction rate
0.71 (2024 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
7.8% of GDP (2020)
Physician density
3.47 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Hospital bed density
5.5 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 99.5% of population
rural: 98.4% of population
total: 99% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.5% of population
rural: 1.6% of population
total: 1% of population (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: intermediate (2023)
vectorborne diseases: tickborne encephalitis
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 9.64 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 4.75 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.52 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.37 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.36 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
comparison ranking: total 25
Tobacco use
total: 36.9% (2020 est.)
male: 37.6% (2020 est.)
female: 36.1% (2020 est.)
comparison ranking: total 11
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
50.8% (2023 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.4%
male: 99.7%
female: 99.2% (2021)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 15 years
male: 14 years
female: 16 years (2020)
Environment
Environment - current issues
air pollution improving but still a concern in urban settings and in emissions arriving from neighboring countries; surface water pollution in the Danube River Basin
Environment - international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Multi-effect Protocol, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Climate
Mediterranean and continental; continental climate predominant with hot summers and cold winters; mild winters, dry summers along coast
Land use
agricultural land: 23.7% (2018 est.)
arable land: 16% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 6.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 34.4% (2018 est.)
other: 41.9% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 58.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.05% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 15.29 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 17.49 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 3.98 megatons (2020 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1.654 million tons (2015 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 269,933 tons (2015 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 16.3% (2015 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Dunav (Danube) (shared with Germany [s], Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Serbia, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania [m]) - 2,888 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 460 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
industrial: 700 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
agricultural: 80 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
Total renewable water resources
105.5 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
Geoparks
total global geoparks and regional networks: 3 (2024)
global geoparks and regional networks: Biokovo-Imotski Lakes; Papuk; Vis Archipelago (2024)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Croatia
conventional short form: Croatia
local long form: Republika Hrvatska
local short form: Hrvatska
former: People's Republic of Croatia, Socialist Republic of Croatia
etymology: name derives from the Croats, a Slavic tribe who migrated to the Balkans in the 7th century A.D.
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Zagreb
geographic coordinates: 45 48 N, 16 00 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the name seems to be related to "digging"; archeologists suggest that the original settlement was established beyond a water-filled hole or graba and that the name derives from this; za in Slavic means "beyond"; the overall meaning may be "beyond the trench (fault, channel, ditch)"
Administrative divisions
20 counties (zupanije, zupanija - singular) and 1 city* (grad - singular) with special county status; Bjelovarsko-Bilogorska (Bjelovar-Bilogora), Brodsko-Posavska (Brod-Posavina), Dubrovacko-Neretvanska (Dubrovnik-Neretva), Istarska (Istria), Karlovacka (Karlovac), Koprivnicko-Krizevacka (Koprivnica-Krizevci), Krapinsko-Zagorska (Krapina-Zagorje), Licko-Senjska (Lika-Senj), Medimurska (Medimurje), Osjecko-Baranjska (Osijek-Baranja), Pozesko-Slavonska (Pozega-Slavonia), Primorsko-Goranska (Primorje-Gorski Kotar), Sibensko-Kninska (Sibenik-Knin), Sisacko-Moslavacka (Sisak-Moslavina), Splitsko-Dalmatinska (Split-Dalmatia), Varazdinska (Varazdin), Viroviticko-Podravska (Virovitica-Podravina), Vukovarsko-Srijemska (Vukovar-Syrmia), Zadarska (Zadar), Zagreb*, Zagrebacka (Zagreb county)
Independence
25 June 1991 (from Yugoslavia); note - 25 June 1991 was the day the Croatian parliament voted for independence; following a three-month moratorium to allow the European Community to solve the Yugoslav crisis peacefully, parliament adopted a decision on 8 October 1991 to sever constitutional relations with Yugoslavia; notable earlier dates: ca. 925 (Kingdom of Croatia established); 1 December 1918 (Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (Yugoslavia) established)
National holiday
Statehood Day (National Day), 30 May (1990); note - marks the day in 1990 that the first modern multi-party Croatian parliament convened
Legal system
civil law system influenced by legal heritage of Austria-Hungary; note - Croatian law was fully harmonized with the European Community acquis as of the June 2010 completion of EU accession negotiations
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 22 December 1990
amendments: proposed by at least one fifth of the Assembly membership, by the president of the republic, by the Government of Croatia, or through petition by at least 10% of the total electorate; proceedings to amend require majority vote by the Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; passage by petition requires a majority vote in a referendum and promulgation by the Assembly; amended several times, last in 2014
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Croatia
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Zoran MILANOVIC (since 18 February 2020)
head of government: Prime Minister Andrej PLENKOVIC (since 19 October 2016)
cabinet: Council of Ministers named by the prime minister and approved by the Assembly
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 December 2019 with a runoff on 5 January 2020 (next to be held in 2024); the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the president and approved by the Assembly
election results:
2019: Zoran MILANOVIC elected president in second round; percent of vote in second round - Zoran MILANOVIC (SDP) 52.7%, Kolinda GRABAR-KITAROVIC (HDZ) 47.3%
2015: Kolinda GRABAR-KITAROVIC elected president in second round; percent of vote in second round - Kolinda GRABAR-KITAROVIC (HDZ) 50.7%, Ivo JOSIPOVIC (Forward Croatia Progressive Alliance) 49.3%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Assembly or Hrvatski Sabor (151 seats; 140 members in 10 multi-seat constituencies and 3 members in a single constituency for Croatian diaspora directly elected by proportional representation vote using the D'Hondt method with a 5% threshold; an additional 8 members elected from a nationwide constituency by simple majority by voters belonging to minorities recognized by Croatia; the Serb minority elects 3 Assembly members, the Hungarian and Italian minorities elect 1 each, the Czech and Slovak minorities elect 1 jointly, and all other minorities elect 2; all members serve 4-year terms
elections: last election held on 17 April 2024 (next to be held by April 2028)
election results: percent of vote by party/coalition - HDZ-led coalition 40.4%, SDP 27.8%, DP 9.3%, MOST 7.3%, We Can! 6.6%, SDSS 2.0%, Independents 1.3%, NPS 1.3%, IDS 1.3%, Bosniaks Together 0.7%, DZMH 0.7%, Focus 0.7%, SRRH 0.7%; seats by party/coalition - HDZ-led coalition 61, SDP 42, DP 14, MOST 11, We Can! 10, SDSS 3, Independents 2, NPS 2, IDS 2, Bosniaks Together 1, DZMH 1, Focus 1, SRRH 1; composition - men 101, women 50, percent of women 33%
note: on 14 March 2024, the Assembly voted unanimously to dissolve, prompting the April 2024 snap election
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president and vice president, 25 civil department justices, and 16 criminal department justices)
judge selection and term of office: president of Supreme Court nominated by the president of Croatia and elected by the Sabor for a 4-year term; other Supreme Court justices appointed by the National Judicial Council; all judges serve until age 70
subordinate courts: Administrative Court; county, municipal, and specialized courts; note - there is an 11-member Constitutional Court with jurisdiction limited to constitutional issues but is outside of the judicial system
Political parties
Bosniaks Together
The Bridge or MOST (formerly the Bridge of Independent Lists)
Croatia Romani Union Kali Sara (SRRH)
Croatian Democratic Union or HDZ
Democratic Union of Hungarians in Croatia (DZMH)
Focus or Fokus
Homeland Movement or DP (also known as Miroslav Škoro Homeland Movement or DPMS)
Independent Democratic Serb Party or SDSS
Independent Platform of the North (NPS)
Istrian Democratic Assembly or IDS
Social Democratic Party of Croatia or SDP
We Can! or Mozemo!
International organization participation
AIIB, Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EMU, EU, FAO, G-11, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, NAM (observer), NATO, NSG, OAS (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMOGIP, UNWTO, UPU, Wassenaar Arrangement, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Pjer ŠIMUNOVIĆ (since 8 September 2017)
chancery: 2343 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 588-5899
FAX: [1] (202) 588-8937
email address and website:
washington@mvep.hr
https://mvep.gov.hr/embassy-114969/114969
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, New York, Seattle (WA)
consulate(s): Anchorage (AL), Houston, Kansas City (MO),Minneapolis/St. Paul (MN), New Orleans, Pittsburgh (PA)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Nathalie RAYES (since 25 January 2024)
embassy: Ulica Thomasa Jeffersona 2, 10010 Zagreb
mailing address: 5080 Zagreb Place, Washington DC 20521-5080
telephone: [385] (1) 661-2200
FAX: [385] (1) 665-8933
email address and website:
ZagrebACS@state.gov
https://hr.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and blue - the Pan-Slav colors - superimposed by the Croatian coat of arms; the coat of arms consists of one main shield (a checkerboard of 13 red and 12 silver (white) fields) surmounted by five smaller shields that form a crown over the main shield; the five small shields represent five historic regions (from left to right): Croatia, Dubrovnik, Dalmatia, Istria, and Slavonia
note: the Pan-Slav colors were inspired by the 19th-century flag of Russia
National symbol(s)
red-white checkerboard; national colors: red, white, blue
National anthem
name: "Lijepa nasa domovino" (Our Beautiful Homeland)
lyrics/music: Antun MIHANOVIC/Josip RUNJANIN
note: adopted in 1972 while still part of Yugoslavia; "Lijepa nasa domovino," whose lyrics were written in 1835, served as an unofficial anthem beginning in 1891
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 10 (8 cultural, 2 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Plitvice Lakes National Park (n); Historic Split (c); Old City of Dubrovnik (c); Euphrasian Basilica; Historic Trogir (c); Šibenik Cathedral (c); Stari Grad Plain (c); Zadar and Fort St. Nikola Venetian Defense Works (c); Primeval Beech Forests (n); Stećci Medieval Tombstones Graveyards (c)
Economy
Economic overview
tourism-based economy that was one of the hardest hit by COVID-19 economic disruptions; newest euro user since 2023, helping recover from a 6-year recession; public debt increases due to COVID-19 and stimulus packages; weak exports; continuing emigration; new liquefied natural gas import terminal
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$159.305 billion (2023 est.)
$154.574 billion (2022 est.)
$144.425 billion (2021 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
comparison ranking: 81
Real GDP growth rate
3.06% (2023 est.)
7.03% (2022 est.)
13.04% (2021 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
comparison ranking: 107
Real GDP per capita
$41,300 (2023 est.)
$40,100 (2022 est.)
$37,200 (2021 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
comparison ranking: 59
GDP (official exchange rate)
$82.689 billion (2023 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
7.94% (2023 est.)
10.78% (2022 est.)
2.55% (2021 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
comparison ranking: 154
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: BBB- (2019)
Moody's rating: Ba1 (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: BBB- (2019)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 3.7% (2017 est.)
industry: 26.2% (2017 est.)
services: 70.1% (2017 est.)
comparison rankings: services 69; industry 107; agriculture 143
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 57.3% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 19.5% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 20% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 51.1% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -48.8% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
maize, wheat, maize, sugar beets, milk, barley, soybeans, sunflower seeds, grapes, pork (2022)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Industries
chemicals and plastics, machine tools, fabricated metal, electronics, pig iron and rolled steel products, aluminum, paper, wood products, construction materials, textiles, shipbuilding, petroleum and petroleum refining, food and beverages, tourism
Industrial production growth rate
-0.47% (2023 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
comparison ranking: 160
Labor force
1.744 million (2023 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
comparison ranking: 132
Unemployment rate
6.06% (2023 est.)
6.96% (2022 est.)
7.61% (2021 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
comparison ranking: 123
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 19.2% (2023 est.)
male: 17.3% (2023 est.)
female: 22.3% (2023 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
comparison ranking: total 67
Population below poverty line
18% (2021 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
28.9 (2021 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
comparison ranking: 131
Average household expenditures
on food: 19.6% of household expenditures (2021 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 6.6% of household expenditures (2021 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3.1% (2021 est.)
highest 10%: 22.3% (2021 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Remittances
6.89% of GDP (2023 est.)
7.51% of GDP (2022 est.)
7.23% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Budget
revenues: $212.81 billion (2019 est.)
expenditures: $211.069 billion (2019 est.)
Public debt
82.08% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
comparison ranking: 38
Taxes and other revenues
21.41% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
comparison ranking: 72
Current account balance
$956.968 million (2023 est.)
-$2.336 billion (2022 est.)
$651.685 million (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
comparison ranking: 57
Exports
$44.969 billion (2023 est.)
$41.903 billion (2022 est.)
$34.367 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
comparison ranking: 69
Exports - partners
Italy 13%, Slovenia 11%, Germany 11%, Hungary 10%, Bosnia and Herzegovina 9% (2022)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Exports - commodities
refined petroleum, electricity, natural gas, garments, wood (2022)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Imports
$46.571 billion (2023 est.)
$46.664 billion (2022 est.)
$36.256 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
comparison ranking: 70
Imports - partners
Italy 14%, Germany 12%, Slovenia 11%, Hungary 7%, US 7% (2022)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Imports - commodities
natural gas, refined petroleum, electricity, garments, cars (2022)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.176 billion (2023 est.)
$29.726 billion (2022 est.)
$28.309 billion (2021 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
comparison ranking: 62
Exchange rates
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
0.925 (2023 est.)
0.95 (2022 est.)
0.845 (2021 est.)
0.876 (2020 est.)
0.893 (2019 est.)
note: Croatia used the kuna prior to conversion to the euro on 1 January 2023. During the transition period the exchange rate was fixed at 7.53450 kuna to 1 euro.
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2022 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 5.417 million kW (2022 est.)
consumption: 17.111 billion kWh (2022 est.)
exports: 7.226 billion kWh (2022 est.)
imports: 11.92 billion kWh (2022 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.729 billion kWh (2022 est.)
comparison rankings: transmission/distribution losses 118; imports 23; exports 30; consumption 80; installed generating capacity 86
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 36.4% of total installed capacity (2022 est.)
solar: 1.1% of total installed capacity (2022 est.)
wind: 16.2% of total installed capacity (2022 est.)
hydroelectricity: 38.3% of total installed capacity (2022 est.)
geothermal: 0.4% of total installed capacity (2022 est.)
biomass and waste: 7.5% of total installed capacity (2022 est.)
Coal
consumption: 702,000 metric tons (2022 est.)
exports: 1,000 metric tons (2022 est.)
imports: 702,000 metric tons (2022 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 11,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 70,000 bbl/day (2022 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 71 million barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 741.456 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
consumption: 2.502 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
exports: 1.038 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
imports: 3.006 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
proven reserves: 24.919 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
15.944 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2022 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 1.563 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2022 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 9.474 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2022 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 4.907 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2022 est.)
comparison ranking: total emissions 94
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1.235 million (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 31 (2022 est.)
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 66
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4.48 million (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 111 (2022 est.)
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 129
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: the mobile market is served by three MNOs, supplemented by a number of MVNOs; the network operators have focused on improving ARPU by encouraging prepaid subscribers to migrate to postpaid plans, and on developing revenue from mobile data services; 5G services are widely available, though the sector will only show its full potential later in 2021 following the award of licenses in several bands; this will contribute towards the government’s national broadband plan to 2027, which is tied to the EC’s two allied projects aimed at providing gigabit connectivity by the end of 2025; the broadband sector benefits from effective competition between the DSL and cable platforms, while there are also numerous fiber deployments in urban areas; the number of FttP subscribers broached 134,000 in March 2021. (2021)
domestic: fixed-line teledensity 31 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone subscriptions are 108 per 100 (2021)
international: country code - 385; the ADRIA-1 submarine cable provides connectivity to Albania and Greece; digital international service is provided through the main switch in Zagreb; Croatia participates in the Trans-Asia-Europe fiber-optic project, which consists of 2 fiber-optic trunk connections with Slovenia and a fiber-optic trunk line from Rijeka to Split and Dubrovnik (2019)
Broadcast media
the national state-owned public broadcaster, Croatian Radiotelevision, operates 4 terrestrial TV networks, a satellite channel that rebroadcasts programs for Croatians living abroad, and 6 regional TV centers; 2 private broadcasters operate national terrestrial networks; 29 privately owned regional TV stations; multi-channel cable and satellite TV subscription services are available; state-owned public broadcaster operates 4 national radio networks and 23 regional radio stations; 2 privately owned national radio networks and 117 local radio stations (2019)
Internet users
total: 3.321 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 81% (2021 est.)
comparison ranking: total 115
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1,030,973 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 25 (2020 est.)
comparison ranking: total 73
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 18
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 2,093,577 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 530,000 (2018) mt-km
Heliports
4 (2024)
Pipelines
2,410 km gas, 610 km oil (2011)
Waterways
4,714 km (2022) Danube 2,859 km, Sava 562 km, Drava 505 km, Neretva 20 km, Bosut 151 km, Kupa 296 km, Mura 53 km, Korana 134 km, Lonja 134 km
comparison ranking: 25
Merchant marine
total: 384 (2023)
by type: bulk carrier 10, general cargo 32, oil tanker 14, other 328
comparison ranking: total 50
Ports
total ports: 16 (2024)
large: 2
medium: 0
small: 6
very small: 8
ports with oil terminals: 8
key ports: Bakar, Dubrovnik, Omisalj, Rijeka Luka, Rovinj, Sibenik, Split, Zadar
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of the Republic of Croatia (Oruzane Snage Republike Hrvatske, OSRH): Ground Forces (Hrvatska Kopnena Vojska, HKoV), Naval Forces (Hrvatska Ratna Mornarica, HRM; includes Coast Guard), Air Force (Hrvatsko Ratno Zrakoplovstvo, HRZ) (2024)
note: the Ministry of the Interior is responsible for internal security, including law enforcement (Croatia Police) and border security
Military expenditures
1.8% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.8% of GDP (2023)
1.8% of GDP (2022)
2% of GDP (2021)
1.7% of GDP (2020)
comparison ranking: 77
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 14,000 active-duty personnel (10,000 Army; 1,500 Navy; 1,500 Air force; 1,000 joint/other) (2024)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory is a mix of Soviet-era equipment and a growing amount of more modern weapon systems from Western suppliers, including France, Germany, and the US (2024)
Military service age and obligation
18-27 years of age for voluntary military service; conscription abolished in 2008 (2024)
note: as of 2021, women comprised nearly 15% of the military's full-time personnel
Military deployments
150 Kosovo (KFOR/NATO); 175 Lithuania (NATO; Croatia also has a few hundred personnel participating in several other EU, NATO, and UN missions (2024)
Military - note
the Armed Forces of Croatia (OSRH) are responsible for the defense of Croatia’s sovereignty and territory, contributing to international humanitarian, peacekeeping, and security missions, and providing assistance to civil authorities for such missions as responding to disasters, search and rescue, anti-terrorism, and internal security in times of crisis if called upon by the prime minister or the president; Croatia joined NATO in 2009, and the OSRH participates in NATO missions, including its peacekeeping force in Kosovo and the Enhanced Forward Presence mission in Eastern Europe; it also contributes to EU and UN missions; the OSRH trains regularly with NATO and regional partners
the OSRH was established in 1991 from the Croatian National Guard during the Croatian War of Independence (1991-95); during the war, the ground forces grew to as many as 60 brigades and dozens of independent battalions, and a single military offensive against Serbian forces in 1995 included some 100,000 Croatian troops; in 2000, Croatia initiated an effort to modernize and reform the OSRH into a small, professional military capable of meeting the challenges of NATO membership (2024)
Transnational Issues
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 24,525 (Ukraine) (as of 29 February 2024)
stateless persons: 2,889 (2022)
note: 843,010 estimated refugee and migrant arrivals (January 2015-September 2023)
Illicit drugs
drug trafficking groups are major players in the procurement and transportation of large quantities of cocaine destined for European markets